After only three days, Facebook has temporarily disabled a new feature that would enable applications to ask users for access to their home addresses and mobile phone numbers. In a post on the social site’s Developer Blog, employee Douglass Purdy explains that the feature will return, but will first be retooled to give users greater control over their contact information.
“Over the weekend, we got some useful feedback that we could make people more clearly aware of when they are granting access to this data,” said Purdy. “We agree, and we are making changes to help ensure you only share this information when you intend to do so. We’ll be working to launch these updates as soon as possible, and will be temporarily disabling this feature until those changes are ready. We look forward to re-enabling this improved feature in the next few weeks.”
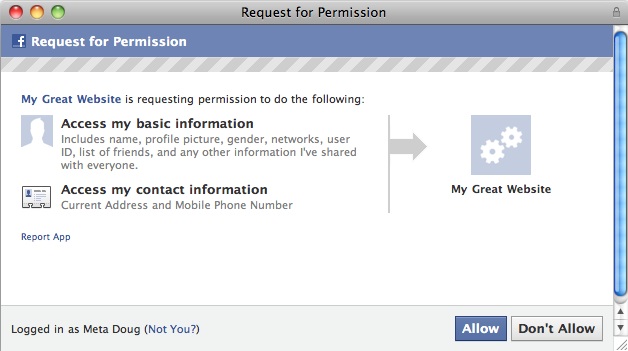
Yesterday, we explained the details and problems with the new feature. Basically, Facebook gave apps permission to ask you if they will “allow” personal data to be shared like home address and mobile number. However, it was rigged so that these permissions could be lumped in with a blanket “Allow” or “Don’t Allow” screen when users first install any app. So to use the app, you have to give it access to your address and phone number even though it’s highly unlikely any app needs that information to run properly. More than likely, most apps would only use such information for ad and sales purposes.
It’s good to see Facebook responding to criticisms in a timely manner. It shows that the site is learning from its mistakes and capable of defending its users, given enough public outrage. However, it would be nice if it didn’t take a bunch of security experts, blogs, and Websites decrying a new feature to get Facebook to care. It should be thinking about privacy issues before it releases features, not after.


