Japan’s high-tech space junk collector appears to have fallen at the first hurdle after the country’s space agency, JAXA, admitted on Tuesday that efforts to deploy the vital “fishing net” component had so far failed.
The unmanned Kounotori 6 spacecraft departed from the International Space Station (ISS) over the weekend and on Tuesday was supposed to begin its first trial run to clear up some of the trash orbiting Earth.
If it’d successfully deployed, the net — essentially a 700-meter-long electrodynamic tether comprising thin wires of stainless steel and aluminum — would’ve created a magnetic force strong enough to affect the movement of targeted trash, slowing it down and causing its orbit to decay. The idea is that the junk would burn up as it entered Earth’s atmosphere.
But despite JAXA’s best efforts, the all-important tether has so far failed to extend.
The agency promised it would carry on trying to get its experimental technology up and running, though it only has until the weekend as the spacecraft is set to disintegrate when it re-enters Earth’s atmosphere on Monday.
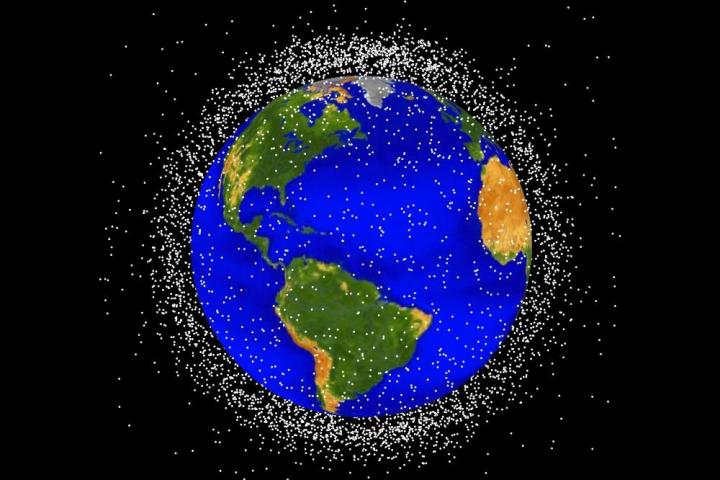
Space junk left behind during five decades of space exploration is becoming a serious issue. Old orbiters, pieces of disused rockets, and a large number of fragments created by collisions are all orbiting our planet, creating a dangerous hazard for the ISS inhabitants and satellites, as well as future space missions.
NASA says “many millions” of pieces of space debris are currently orbiting Earth, with around 20,000 fragments larger than a softball.
“They travel at speeds up to 17,500 mph, fast enough for a relatively small piece of orbital debris to damage a satellite or a spacecraft,” the U.S. space agency reports on its website.
Other proposed solutions for clearing up space junk include laser systems, solar-sail “parachutes,” trash-eating spacecraft, and targeted air puffs designed, like JAXA’s experimental system, to force the junk to de-orbit and burn up in Earth’s atmosphere.
But as things stand, all that space garbage looks like it could be circling our planet for some time to come.


