The project is known as METI (Messaging Extraterrestrial Intelligence) and it actively seeks to send greetings to any alien civilizations out there, as opposed to SETI (Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence) which passively looks for signs of life beyond our solar system. It’s a controversial program, to say the least. Physicist Stephen Hawking, one of its most vociferous opponents, has famously warned against such an endeavor: “If aliens visit us, the outcome would be much as when Columbus landed in America, which didn’t turn out well for the Native Americans.”
In an interview with Newsweek, the president of METI, Douglas Vakoch, tried to assuage the concerns raised about the program. “Any civilization that could travel to Earth to do us harm could already pick up our leakage television and radio signals,” he said. “So there’s no increased risk of alerting them of our existence.”
Dan Werthimer, a SETI researcher at Berkeley, told New Scientist: “It’s like shouting in a forest before you know if there are tigers, lions, and bears or other dangerous animals there.”
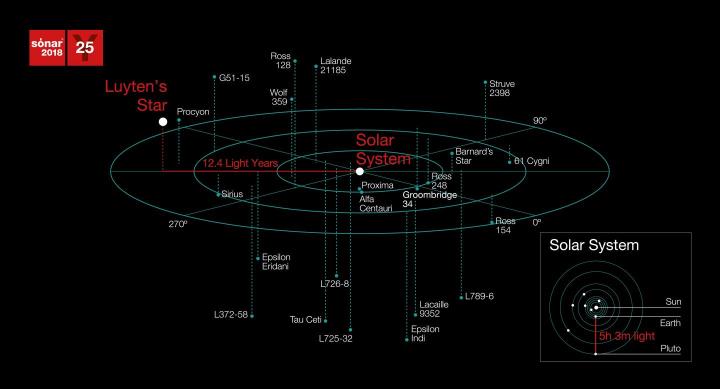
The system that’s the target of the message is a red dwarf designated GJ273, also known as Luyten’s Star in the Canis Minor constellation, with an exoplanet GJ273b that could possibly support life. It’s 12.4 light years away, and in the message researchers said they’d be looking for a response 25 years in the future.
Then there’s the question of exactly how we communicate with aliens. The Voyager missions famously carried a golden record that was filled with the sounds of Earth, as well as an interstellar map that might lead aliens back to our planet.
“Extraterrestrials won’t speak English or Spanish or Swahili,” said Vakoch. “Our message is written in the language of math and science. Over the centuries, scientists and mathematicians have repeatedly taken a vote on the most essential concepts needed to explain the nature of the universe.”
The message was beamed three times to the system, on October 16, 17, and 18. Each transmission took 11 minutes. The invite also includes a cosmic clock, indicating how much time has passed between transmissions. It’s hoped that the aliens can decipher the message and send back a reply. Another message is planned to the same star, which will include the date we’re expecting a reply.
So, set your calendars for June 21, 2043. It could be a big day for humanity.


