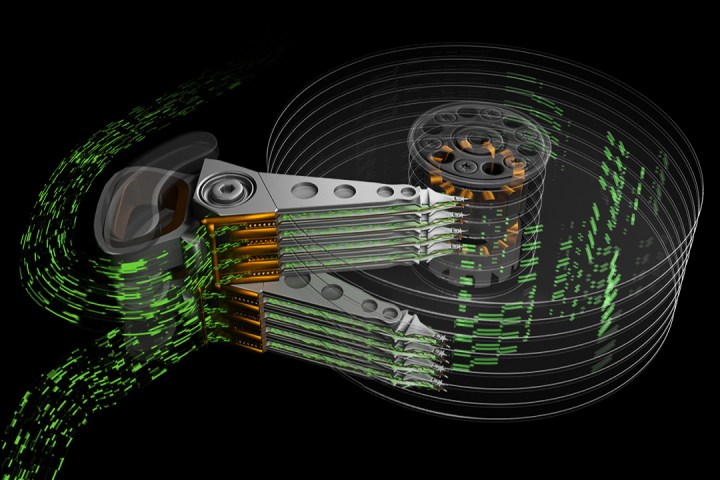
On their simplest level, hard drives are similar to old-school record players, only they can write to the medium as well. Hard drives contain several magnetic, spinning “records” that hold your data, and are accessed by arms with needle-style readers on their ends. These arms typically move across the platters simultaneously, but Seagate’s multi-actuator technology now divides them all into two separate groups.
“With two actuators operating on a single pivot point, each actuator will control half of the drive’s arms. Half the drive’s recording heads will operate together as a unit, while the other half will operate independently as a separate unit,” Seagate said. “This enables a hard drive to double its performance while maintaining the same capacity as that of a single actuator drive.”
In an illustration, Seagate shows eight spinning platters complemented by eight arms, each with their own read and write heads (needles). All eight share the same pivot point, but the top four are moving separately than the bottom four. Data is read and written at a faster rate because Seagate’s new design doesn’t perform these operations in a single wave, but rather in two using a leapfrog-type fashion.
Seagate’s multi-actuator technology focuses on the hyperscale data center where hard drives are still the major source of storage due to their low cost and extremely high capacities. But they’re not exactly fast when compared to solid-state drives using the same storage device connector. How this new technology will improve access times versus using the standard data center-focused hard drive still remains to be seen.
Unfortunately, the old-school SATA 3 connector used by bulky hard drives and 2.5-inch solid-state drives will always bottleneck performance. You can check our SATA guide if you’re interested in further information. It’s capable of moving data at up to 600MB per second, which you will never experience although 2.5-inch solid state drives can come close. Hard drives with platters that spin up to 7,200 rotations per minute (RPM) can reach up to 160MB per second, and those that spin at 5,400RPM are even slower.
In theory, Seagate’s new technology should double the maximum data movement speed of hard drives. But the new design likely isn’t just locked to splitting the arms into two separate groups: The company likely needed a new controller that can split data into two groups of platters while keeping all that data “together.” In other words, instead of saving your photo to the hard drive in one long stroke, its painted onto the platters in two small, faster strokes.
Seagate also said it developed a new heat-assisted magnetic recording technology (HAMR) to pack even more storage. This tech will appear in its Exos hard drives in pilot volumes during 2018 followed by a full release in 2019.


