One day, in the not-too-distant future, we could well be zipping about the skies in our very own personal flying machines. It may sound like the stuff of science fiction, but Boeing, a company that knows a thing or two about keeping objects airborne, said in March that electric-powered passenger drones could be on the market within a decade.
Boeing is so confident that urban vehicles are about to transform the city landscape that last year the company sponsored the GoFly design contest to the tune of $2 million.
Aimed at encouraging innovative designs for ultra-compact personal flying vehicles, entries had to be able to take off and land vertically, and fly for at least 20 miles without recharging.
Teams from 30 countries submitted their efforts, and this week the organizers revealed the 10 winners who now have to transform their drawings into real, fully functional aircraft.
Chosen by an international panel of judges that included chief engineers, flight test engineers, pilots, and esteemed academics, the winning designs range from the familiar to the outright wacky.
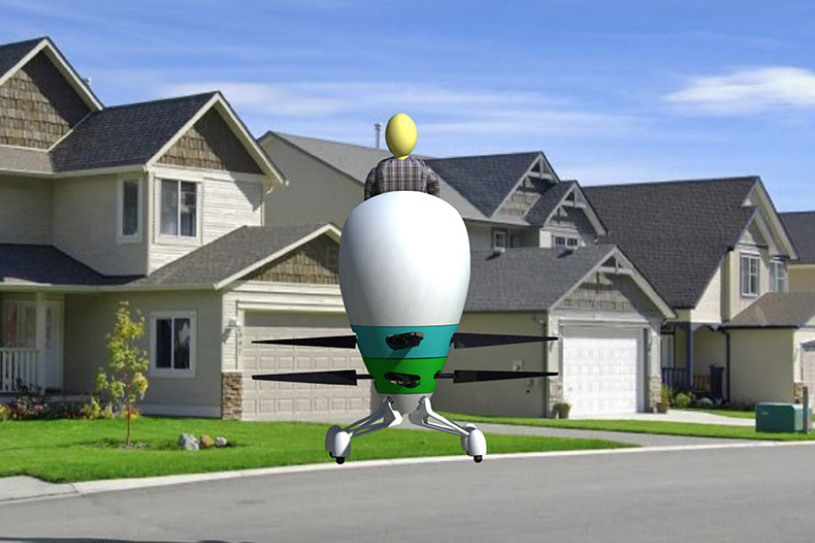
Take, for example, Texas A&M University’s Harmony, described as a “compact rotorcraft designed to minimize noise and maximize efficiency, safety, reliability, and flight experience.” It’s the only design among the winners where you seem to have to stand upright in a kind of pod, making for a different kind of flying experience.
Aeroxo LV from Latvia came up with the Era Aviabike, which looks like a cross between a plane and a motorbike, while Georgia Tech’s HummingBuzz appears to place the rider directly over one very large rotor blade. A protective grill serves to eliminate the chance of any troublesome decapitations during flight.
The multimillion-dollar prize fund will be handed out gradually over the next year — the 10 winners of this first stage of the contest have each collected $20,000 to help make their designs a reality.
Phase two of the contest, where teams build prototypes, is actually open to newcomers as well, so the winning design could be one we haven’t even seen yet.
The teams behind the best four prototypes will each pick up a further $50,000 next spring, and the overall winner will be announced at the Final Fly-off event in the fall of 2019.
Interest is clearly growing in the idea of small, electric-powered, urban-compatible aircraft that are quieter and easier to handle than a helicopter.
Airbus-backed Vahana, for example, is developing self-piloting air taxi, and you may have already seen the 184 flying machine from Chinese firm EHang. Uber is working on its own aerial vehicle, as are Joby Aviation, Volocopter, and Kitty Hawk.