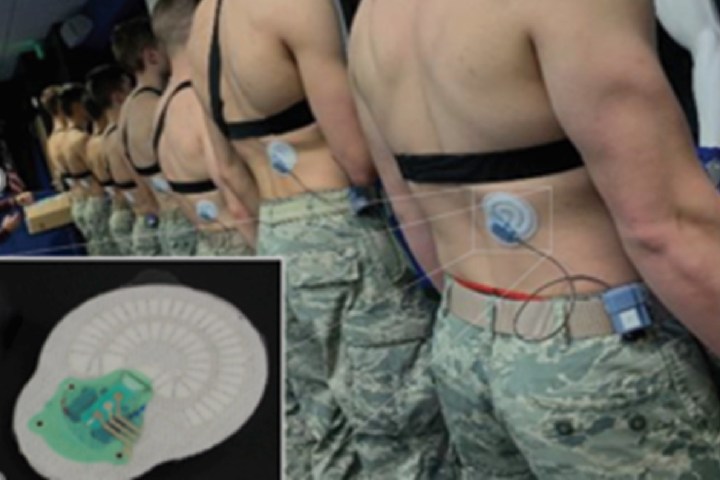
With a job that frequently involves carrying heavy equipment in inhospitable environments, it’s no wonder that military servicemen and women run the risk of dehydration. Capable of causing symptoms which range from chills and muscles cramps through seizures and severe chest pains, dehydration occurs in the human body when it’s lost around 2% of its total fluid. While the only solution to dehydration is increasing fluid level through ingesting liquid, a new smart patch promises to play an important role too, by warning when a person is becoming dangerously dehydrated.
The smart patch in question was developed by researchers at GE Global Research, Binghamton University, UConn, NextFlex, and the Air Force Research Laboratory. Featuring flexible electronics, it attaches to the body and continuously measures its wearer’s hydration levels. It does this by analyzing potassium and sodium in the sweat, in addition to their sweat rate. As well as helping soldiers, its creators think it could be used to help battle dehydration in people working outside as well as athletes.
“What is special is that these measurements are done in real-time and on a continuous and non-obtrusive basis,” Azar Alizadeh, principal scientist at GE Global Research, told Digital Trends. “The raw electrical signals corresponding to the sweat volume sensor and the two electrolyte sensors are transmitted wirelessly to an external mobile device, where through an app the person can track his or her sweat rate and sweat electrolyte levels without any interference with what he or she was doing. Just like we can track heart rate or steps with a fitness device in real time, our device can seamlessly measure sweat. Today, this can’t be done as readily without stopping to take measurements such as a urine sample.”
According to Scott Miller, director of Strategic Programs at flexible electronics company NextFlex, there are two main ways of measuring hydration currently. One looks at short-term weight change, while the other focuses on lab measurements of blood or urine electrolyte concentration. The issue with both of these approaches is that they are not real-time, and are impractical for a person going about normal daily activity.
To put the smart patch through its paces, eight members of the Air Force Academy shooting team recently wore them while tackling an assortment of obstacles, including two 1.5-mile ruck marches while carrying 45 pounds of gear.
“Right now [our] activities focus on improving manufacturability and doing testing in the lab and in the field,” Miller continued. “This involves understanding how several categories of end users will use the devices, and what specifically they need is an important immediate outcome. Past that, getting the devices deployed in the field for athletes and the military is a next step.”


