If you have an Nvidia graphics card, then it’s a good idea to learn how to optimize the Nvidia Control Panel. It has a whole range of features that you can tweak to improve performance and stability and give you access to new and exciting features, like Nvidia’s RTX VSR video upscaler. The best Nvidia Control Panel settings can really upgrade your experience, whether you’re looking to game at high frame rates, or just make your GPU work better.
Keep reading to optimize your Nvidia settings in a few quick steps.
Update your drivers
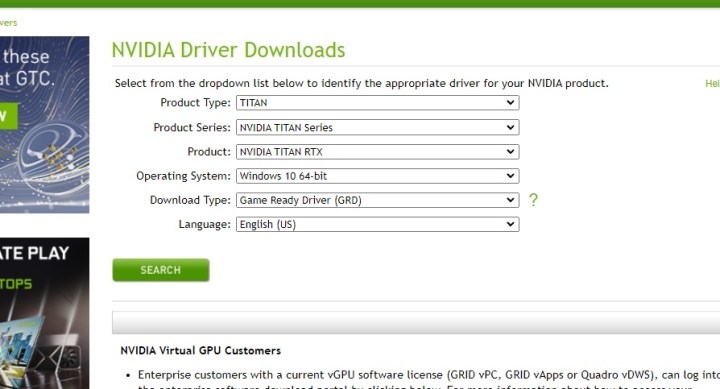
Keeping your drivers up-to-date is the key to getting the best out of your graphics card. Before delving further into the Nvidia Control Panel, make sure that you’ve got the latest drivers that Nvidia has to offer.
You can download the latest Nvidia drivers from the official website. If you need additional help upgrading your drivers, and installing the optional (but useful) GeForce Experience, here’s our guide on updating graphics card drivers.
How to launch the Nvidia Control Panel
There are two ways to launch the Control Panel. The easiest way is to simply right-click on the desktop and choose Nvidia Control Panel from the dropdown menu.
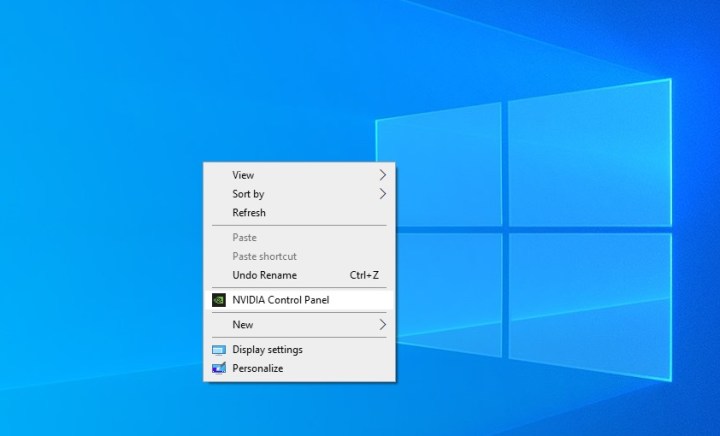
Alternatively, use Windows search to look for Nvidia Control Panel and select the corresponding result.
Best Nvidia Control Panel settings for gaming and performance
You can use individual games’ settings menus to decide your GPU settings, but optimizing your graphics settings in the Control Panel can have a huge impact on your gaming experience. Smoother gameplay and better, sharper, brighter visuals are all a possibility when the settings are properly adjusted.
The Nvidia Control Panel is easy enough to navigate, but there are so many options to choose from, it may seem confusing at first. Let’s take a look at each of the settings and what they do, as well as some suggestions on what you might like to set them to.
Nvidia Control Panel — 3D Settings
The 3D Settings tab on the left-hand side of the Nvidia Control Panel is arguably the most important when it comes to gaming, but it’s equally important for creativity. To access all the options, simply click on Adjust Image Settings With Preview.
Below the moving Nvidia logo, select Use the Advanced 3D Image Settings and then click Apply at the bottom.
Switch to the Manage 3D Settings tab on the left side in order to edit all the available 3D settings.

Image sharpening
This setting enhances the visuals in your games, making them appear sharper and clearer. It doesn’t affect performance but can make your game look crisper like you’re playing at a higher resolution. Too much though, and you’ll lose detail, so don’t go overboard.
A common sharpening level some gamers like is around 0.50 with the film grain set to around 0.17, but feel free to play around.
Ambient occlusion
This setting is responsible for the shadows and environmental lighting in your games.
For the best balance between GPU load and great gameplay, set this to Performance.
Anisotropic filtering
Anisotropic filtering increases the visual quality of game textures when your camera is at a steep angle.
This setting should be set to Application-controlled.
Antialiasing — FXAA
This stands for Fast approximate anti-aliasing which is Nvidia’s screen-space anti-aliasing algorithm. You can turn this setting Off.
Antialiasing — Gamma correction
This corrects the brightness values in images enhanced by antialiasing. It’s usually best to turn this setting On.
Antialiasing — Mode
This is a general setting related to antialiasing, which in itself is a technique that smooths out images. Leave this at Application-Controlled.
Antialiasing — Transparency
The last AA setting applies to Nvidia’s technology of applying antialiasing to transparent textures. You can usually turn this Off.
Background Application Max Frame Rate
This controls the frames per second (fps) that your games and other applications will have when minimized. If you don’t have any performance issues, you can leave this Off.
If you feel you’d rather limit background frame rates, turn this on and set it to the bare minimum frame rate you want to target, such as 60 fps, or on older or weaker GPUs, 30 fps.
CUDA – GPUs
This setting should always be set to All, as it refers to which of the CUDA cores in your graphics card can be used.
DSR – Factors
DSR stands for Dynamic Super Resolution. This technology improves image quality by rendering the images and upscaling them to a higher resolution.
While this sounds good on paper, it’s a killer for your frame rates (fps), so it’s best to turn this setting Off. Especially since newer, more capable solutions like DLSS are now available.
DSR – Smoothness
Much like the previous DSR setting, this will only decrease your fps. As such, it’s better to turn it Off.
Low Latency Mode
Low Latency Mode ensures that the frames in your game are submitted into the render queue just when the graphics card requires them. Nvidia refers to this as “just in time frame scheduling”. This results in, as the name itself suggests, lower latency and higher frame rates.
To increase your fps, turn this setting On.
Max Frame Rate
This setting limits your fps to a certain number. Different games will be able to achieve different fps, and though the true limit of what you can experience will always be your monitor’s refresh rate, some games have heavily unlocked frame rates in menus, which can result in undue power drain on your GPU.
If you don’t want to limit your frame rates in any way, simply turn this setting Off. If you’d like to adjust this setting to match your monitor, keep reading.
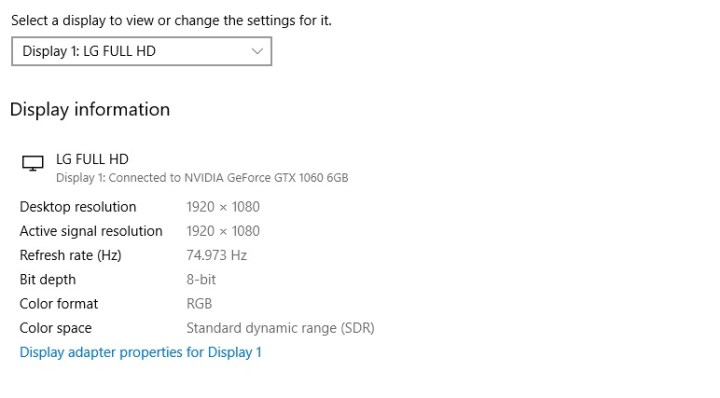
Some competitive gamers like to set this option to double that of their monitor’s refresh rate. If you’re not sure about the refresh rate of your monitor, you can check it in Windows Settings.
In order to check your display’s refresh rate, use Windows search to look for Advanced Display and click on View Advanced Display Info. Check the refresh rate and adjust this setting to match it. In our example, the limit would be 75.
Monitor technology
This setting will not be visible to all users. If you can see it, you can use it to turn on Nvidia’s G-Sync. Nvidia G-Sync is responsible for adjusting your monitor’s refresh rate to become dynamic, causing display refreshes only when a frame is sent from the GPU. It solves issues such as screen tearing.
G-Sync is useful for all high-end and low-end systems, so should be set to On if your monitor supports it.
Multi-Frame Sampled Anti-Aliasing (MFAA)
This setting removes jagged edges and smooths out graphics, resulting in improved visuals. Unfortunately, this is a small gain for the price that your frame rates may have to pay.
For gaming, we recommend that you turn this setting Off.
OpenGL Rendering GPU
This option lets you choose which one of your graphics cards (if you have more than one) will be used for OpenGL. If you have multiple graphics cards, pick your GPU from the dropdown menu and select it.
Power Management Mode
As the name implies, this setting is responsible for optimizing the power vs performance ratio of your graphics card.
If you don’t mind letting your GPU use maximum power and perhaps run a little hotter, select Prefer Maximum Performance.
Shader Cache
When turned on, this setting reduces processor usage. It’s optimal to turn it On.
Texture filtering — Anisotropic sample optimization
Anisotropic sample optimization limits the number of samples that are used by your GPU. Turn this setting On.
Texture filtering — Negative LOD bias
When turned on, this setting makes stationary images sharper and enables texture filtering. Toggle it to Allow.
Texture filtering — Quality
This setting lets you optimize texture filtering to value performance. Switch it to High Performance.
Texture filtering — Trilinear optimization
Trilinear optimization will usually be on by default. It smooths out textures in your games. If it happens to be turned off, make sure to switch it to on.
Threaded optimization
Threaded optimization allows your computer to utilize several processor cores at once. Turn this to Auto.
Triple buffering
When triple buffering is enabled, frames are rendered in one back buffer which can improve frame rates without tearing. Although there are some games that benefit from this setting, it’s best to turn it Off.
Vertical sync
Vsync synchronizes the frame rate with your monitor’s refresh rate. As it can limit your fps and cause input lag, it’s better to turn it Off unless you experience severe screen tearing issues. G-Sync and Freesync are far more capable alternatives.
Virtual Reality pre-rendered frames
This setting limits the number of frames that your processor prepares ahead of your GPU being able to process it.
For optimal performance, set this to 1.
Finishing up
Once you have adjusted all of these settings, click Apply on the bottom right-hand side to save the changes.
Nvidia Control Panel settings – Configure Surround, PhysX
Go back to the menu on the left-hand side and navigate to Configure Surround, PhysX.
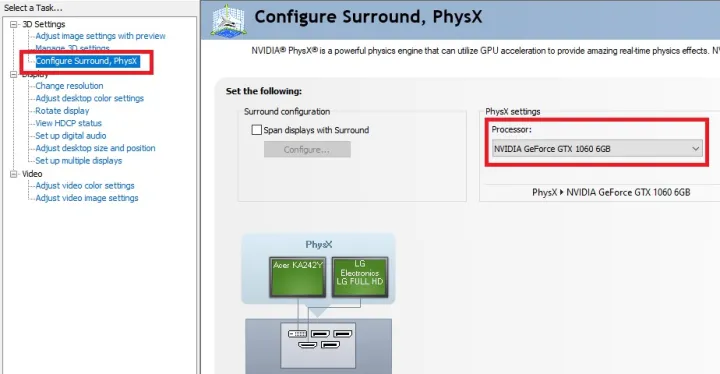
On the right part of this section, you will find PhysX Settings. Switch that from Auto to the model of your GPU.
Nvidia Control Panel settings – Display
This section will help you optimize your display settings. Navigate to it on the left-hand side and go down the list as required.
Change resolution
Select the monitor that you are using at the top of this section. If you have multiple displays, you will have to repeat the steps for all of them.
Under Resolution, scroll down until you find the highest possible resolution in the PC section. Next, adjust the monitor’s refresh rate to the highest available.
Scroll down to the color settings and click on Use Nvidia Color Settings. Make sure that the desktop color depth is set to Highest (32-bit) and that the Output Dynamic Range is set to Full.

Select Apply to save all your changes.
Adjust desktop color settings
This section lets you play around with the color settings on your display. All the settings here are down to your personal preference. You can adjust Brightness, Contrast, and Gamma in the first row. Feel free to move the sliders and press Apply to see the result, as the changes are easily reverted.
You can also try out Digital Vibrance. This setting will increase color saturation and make the shades brighter. A value of around 70% to 80% may look best, but this depends on the game.
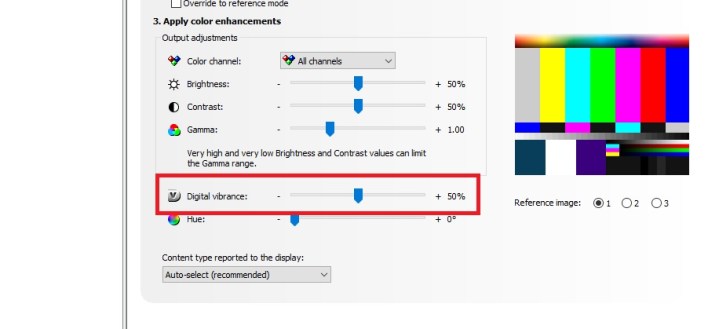
If you’ve made any changes, press Apply.
Adjust desktop size and position
You will notice that we’ve skipped over the next three sections: Rotate display, View HDCP status, and Set Up Digital Audio. All of these have no impact on gaming and won’t require adjustments.
In the Adjust Desktop Size and Position tab, pick the display you want to make changes to, and then look down toward the Scaling section.
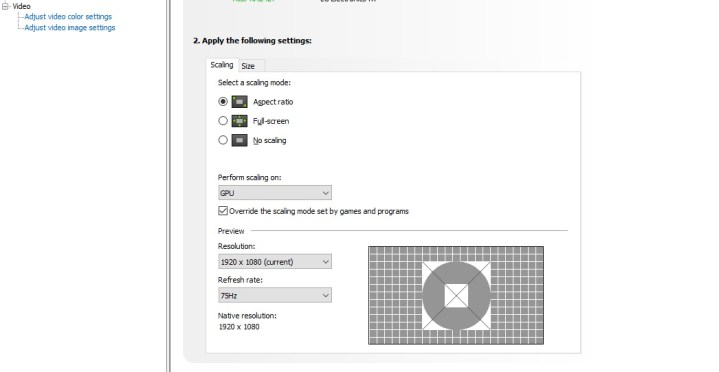
You can choose the correct setting to pick here based on your needs.
- For the highest fps possible at native resolution, pick No Scaling.
- If you want the best mix of performance and visuals, make sure you Enabled GPU Scaling in 3D settings, and then set this option to Aspect ratio.
- For games with low resolutions and pixel games pick Integer Scaling.
Don’t forget to make sure that the scaling is performed on the GPU by selecting that option in the dropdown menu below. Lastly, tick the box that says Override the Scaling Mode Set By Games and Programs.
Once you’re done, press Apply.
Set up G-Sync
Look back at the menu on the left-hand side. If this section is not visible to you, simply move on to the next step. If it is, it will let you decide whether or not to use Nvidia G-Sync.
Nvidia’s G-Sync synchronizes your monitor’s refresh rates to match the graphics card. However, on modern computers with powerful graphics cards and gaming monitors with higher refresh rates, this setting is almost obsolete. It can actually lower your gaming performance.
If you are playing on a budget or mid-range computer that is several years old, you can try out G-Sync by ticking the box next to Enable.
Set up multiple displays
This section is only useful to users who run multiple monitor setups. If that’s not you, jump down to the next step.
In this part of the Control Panel, you will be able to change your display configuration and which displays to use. If you have two or more monitors, you can drag their icons using your mouse. This lets you pick which display will act as your primary monitor.
In general, you should drag the icons to match the physical setup of your displays. You can move them above, below, to the right, or to the left, so all kinds of monitor setups can be configured here.
Adjust video color settings
This setting will help you optimize the color palette used in videos and games.
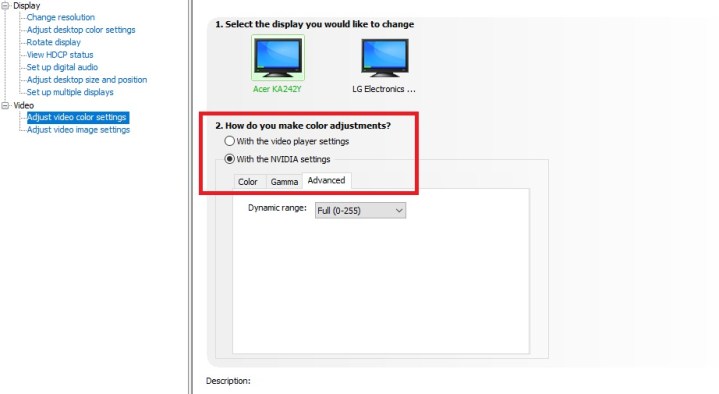
In the second question about color adjustments choose the second option — Nvidia Settings. Switch over to the Advanced tab below. Pick Full (0-255) and press Apply to save all changes.
Adjust Video Image Settings

The Nvidia Control Panel also lets you adjust the way video is displayed. It features one of the newest Nvidia features: RTX Video Super Resolution, or VSR. This setting can be enabled under the RTX video enhancement heading, and automatically upscales any video you watch online using your Nvidia GPU’s Tensor cores. It only works with RTX 30-series and RTX 40-series GPUs for now, though may be made available for RTX 20-series GPUs in the future.
It’s not a game-changing setting, so you don’t need to use it, but it does make lower-resolution video look sharper, so enable it if you think you’ll benefit from that. We have some more tips on using it in our how to use RTX VSR guide.
Finalize the changes
Your PC should now be running on the best Nvidia Control Panel settings for gaming and overall performance.
In order to finalize the changes, restart your computer. Once that’s done, run your favorite game and check to make sure that everything is stable. Feel free to go back to the Nvidia Control Panel to tweak the settings further if needed.
What settings should you change in the Nvidia Control Panel?
If you want to quickly adjust your settings to increase frames per second and offer smooth gameplay, but don’t necessarily need to know what each setting does, here are the settings you should change.
3D Settings
- Image sharpening: Turn this On. Set the sharpening level to 0.50 and the film grain to 0.17.
- Ambient occlusion: Set this to Performance.
- Antialiasing — FXAA: Turn this Off.
- Antialiasing — gamma correction: Turn this On.
- Antialiasing — mode: Set this to Application-controlled.
- Antialiasing — transparency: Turn this Off.
- Background application max frame rate: Turn this Off.
- CUDA – GPUS: Set this to All.
- DSR – Factors; DSR – Smoothness: Turn both of these Off.
- Low latency mode: Turn this On.
- Max frame rate: Turn this Off or synchronize it to your monitor’s refresh rate.
- Monitor technology: Turn G-Sync On.
- MFAA: Turn this Off.
- OpenGL Rendering GPU: Pick your GPU from the dropdown menu and select it.
- Power Management Mode: Select Prefer Maximum Performance.
- Shader Cache: Turn this On.
- Texture filtering — anisotropic sample optimization: Turn this On.
- Texture filtering — negative LOD bias: Set this to Allow.
- Texture filtering — quality: Set this to High Performance.
- Texture filtering — trilinear optimization: Turn this On.
- Threaded optimization: Set this to Auto.
- Triple buffering: Turn this Off.
- Vertical sync: Turn this Off.
- Virtual reality pre-rendered frames: Set this to 1.
- Configure surround, PhysX: Switch PhysX to the model of your GPU.
Press Apply to save all changes.
Display settings
Press Apply after completing each step.
- Change resolution: Set the highest possible resolution and the highest refresh rate available. Select Use Nvidia Color Settings and set the color depth to the Highest, and the dynamic range to Full.
- Adjust desktop color settings: Set Digital Vibrance to 70-80% and see if you like it.
- Adjust desktop size and position: Refer to our full explanation to pick the right setting in this section.
- Set up G-Sync: Turn G-Sync On.
- Adjust video color settings: Select the option to Use Nvidia Settings. Pick Full (0-255).
Restart your computer to finalize the changes.




