The MediaTek Dimensity 9000 chipset is intended to launch the Taiwanese chipmaker into the mainstream on the back of performance that rivals the 800-pound gorillas in the room, like Apple’s A15 Bionic and the Qualcomm Snapdragon 888 and 888 Plus mobile platforms. While the new chip appears solid on paper, how well is it actually equipped to take on these competitors? We take a look.
What’s the big deal about Dimensity?
Many smartphone companies are following in Apple’s footsteps, with plans to launch their own systems on a chip (SoC) to cut away from their dependence on a single brand and mitigate the effects of the global semiconductor shortage. As a result, many companies are trying to find their place in a race that is currently led by Qualcomm. Aside from smartphone companies moving production in-house, underdogs like MediaTek are also vying for a share in the flagship market. The result of this is the new and powerful MediaTek Dimensity 9000 chipset, which is tailored to take on the leaders in the segment.

MediaTek’s Dimensity series has already made headlines around the world after being used on popular devices such as the OnePlus Nord 2 and the Realme X7 Max, both of which run the Dimensity 1200. Although high-end, these are not flagship or premium devices, and truth be told, MediaTek hasn’t really had a truly flagship chipset — until now. With the Dimensity 9000, MediaTek aims to challenge the invariable monopoly of the Snapdragon 8xx series in the flagship Android smartphone market.
Dimensity 9000
The MediaTek Dimensity 9000 has many firsts up its sleeves. Besides being the first mobile SoC to be manufactured on a 4nm process, it is the first one to use TSMC’s new N4 design. This design choice gives it an edge over the Snapdragon 888, the Apple A15 Bionic, and the Samsung Exynos 2100 — all of which are based on 5nm designs. Qualcomm’s shift of its chip manufacturing from TSMC to Samsung’s foundries presents an opportunity for MediaTek to fill this gap and benefit significantly because of the smaller node — thus, leading the industry in this respect.
New Core Architecture

The Dimensity 9000 uses 1+3+4 CPU orientation and is also the first mobile SoC to use ARM’s Cortex-X2 core based on ARM’s V9 architecture that was announced in May 2021 as part of the ARM’s new licensable CPU IP. The new IP aims to improve the on-device machine learning applications on new and upcoming chipsets.
The Cortex-X2 is a successor to the Cortex-X1 we have been seen on the Qualcomm Snapdragon 888/888 Plus, Samsung Exynos 2100, and Google Tensor SoC. Besides the Cortex-X2 core, which serves as the primary core with its clock speed of 3.05GHz, the MediaTek 9000 features three Cortex-A710 cores at 2.85GHz for the middle cores and four Cortex-A510 cores at 1.8GHz for the LITTLE (power-efficient) cores. Similar to the Exynos 2100, the cores on Dimensity 9000 have higher frequency than the Snapdragon 888’s Cortex-A78 cores that are clocked at 2.4GHz.
Mali G710 GPU

The MediaTek Dimensity 9000 is also the first chipset to use the Mali-G710 GPU, which features a 10-core configuration as an upgrade over the nine-core GPU on the Dimensity 1200. The company says the cores have a peak frequency of about 850MHz. With Samsung striving to adopt AMD’s RDNA GPUs on its upcoming line of custom Exynos chipset, MediaTek appears to be the only chipmaker adopting the new GPU IP. We expect the performance to exceed the Mali-G78 GPU seen on Google Tensor.
MediaTek claims the GPU will support ray tracing, but the feature is actually implemented through software using an API instead of hardware acceleration.
LPDDR5X RAM
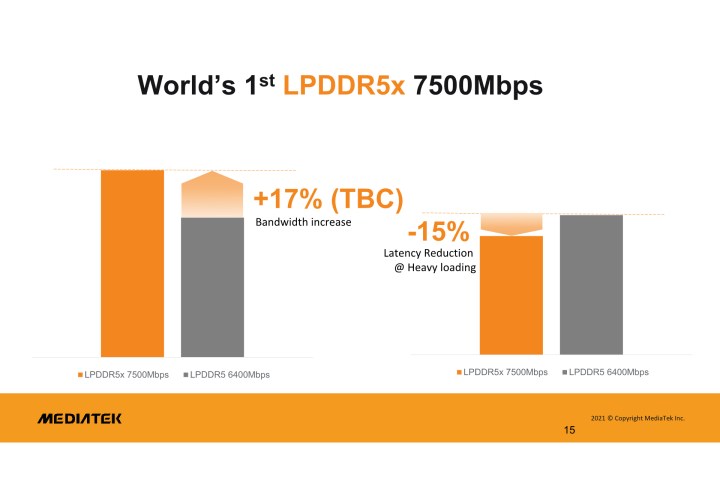
With the Dimensity 9000, MediaTek introduces support for LPDDR5X memory — another first among mobile chipsets. The new LPDDR5X standard for RAM exceeds LPDDR5 with a performance increase of roughly 33%, from 6400Mbps to 8533Mbps. It’s important to note that while the MediaTek chip can only utilize bandwidth up to 7500Mbps, the memory controller is also backward compatible with the previous LPDDR5 RAM standard, giving manufacturers the flexibility to choose based on their performance needs,
The MediaTek Dimensity 9000 also features a 6MB system cache, which is twice as big as what we see on the Snapdragon 888 SoC. This will allow all blocks on the flagship MediaTek chipset to perform much better and be more power efficient.
MediaTek Dimensity 9000 vs. Qualcomm Snapdragon 888
MediaTek is making several claims about its new maxed-out Dimensity 9000, and many of these claims put the chip giant in a favorable position, both from the perspective of manufacturers and consumers. Before we elaborate on those claims, here is a side-by-side comparison between the Dimensity 9000 and the Snapdragon 888, as well as the Snapdragon 888 Plus:
| SoC | MediaTek Dimensity 9000 | Qualcomm Snapdragon 888/888 Plus |
| CPU |
|
|
| GPU | Mali-G710 @ ~850MHz | Adreno 660 @ 840MHz |
| Memory |
|
|
| NPU/APU | 6-core APU | Hexagon 780 |
| ISP | Imagiq790 18-bit ISP
|
Triple 14-bit Spectra 580 ISP
|
| Manufacturing node | TSMC N4 (4nm) | Samsung 5LPE (5nm) |
In terms of CPU performance, MediaTek claims the Dimesnity 9000 offers a 35% performance increase over an Android flagship, which most likely refers to any phone powered by the Snapdragon 888. The smaller node also improves the efficiency by about 37%. This expectedly puts the Dimensity 9000 in a favorable spot not only compared to the Snapdragon 888 but also the alleged Snapdragon 898, which may be called the Snapdragon 8 Gen1 instead and is also rumored to be based on the same CPU IP from ARM, albeit with lower frequencies.
In terms of GPU, MediaTek claims 35% higher performance on the Dimensity 9000 than other flagship Android chipset from its competitors, and we can safely assume the Snapdragon 888 is being referred to here as well. The Dimension 9000 is also touted to bring 60% higher power efficiency with the new Mali GPU it is using. Once again, this claim ensures a secure position for the Dimensity 9000 not only against its existing competitors but also the upcoming ones.
Overall, the Dimensity 9000 will bring a 17% hike in terms of bandwidth and a 15% reduction in latency.
Image processing surpasses current options
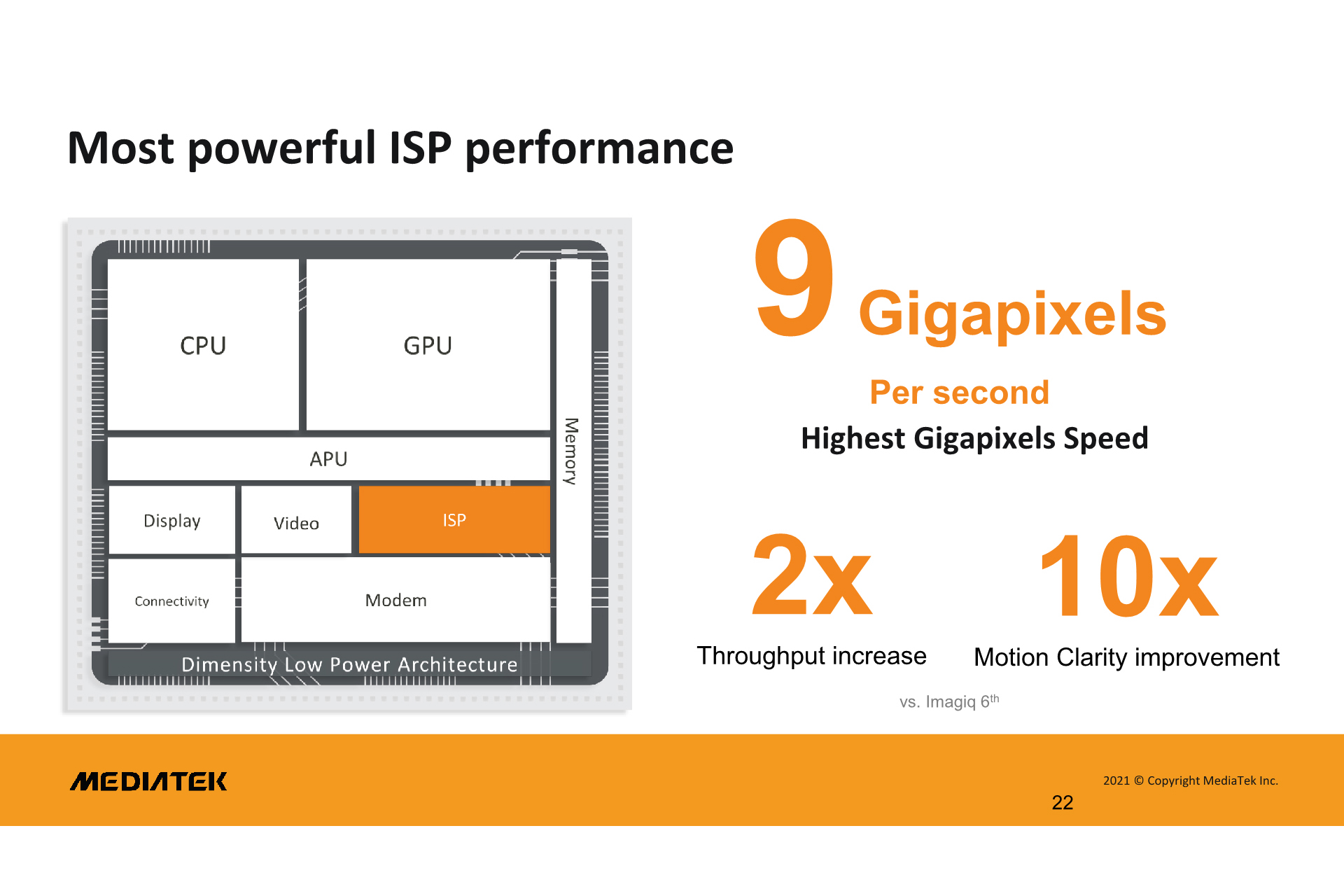
Another excitingaspect of the Dimensity 9000 chipset is that MediaTek is extending support for up to 320-megapixel image sensors on devices powered by it with the new Image Signal Processor (ISP). This not only surpasses the existing chipsets but also transcends the biggest available camera sensors on the smartphone market, which are currently only as big as 200MP(the only sensor to support this resolution is the Samsung HP1). MediaTek is also said to be working with companies that manufacture camera sensors to bring 320MP sensors to the market for smartphone manufacturers and consumers to benefit.
The revamped camera subsystem can process up to nine gigapixels per second, which is claimed to be a 100% increase over the Dimensity 1200. In contrast, Snapdragon 888’s Spectra 580 ISP can only process 2.7 gigapixels each second.
Dimesnity 9000 is MediaTek’s new hope
MediaTek has finally produced a chipset that matches up to other flagship chips from Apple, Qualcomm, Samsung, and Google. Not only is the Dimensity 9000 first in line to benefit from the new IPs from ARM, but it also appears capable of taking on upcoming flagship chipsets like the Snapdragon 898 (or whatever it might be called officially). It puts MediaTek back in the race of flagships for the first time since the launch of the Helio X30 chip in 2017.
In an interview with Digital Trends‘ Andy Boxall, MediaTek’s Vice President of Corporate Marketing Finbarr Moynihan said: “It’s quite a big step forward, but there will be a fairer comparison when true competing products come out next year. That said, based on our architecture and TSMC’s process, we think we will maintain power efficiency advantages next year, but the performance gap may close.”
Moynihan also claims this is a “multiyear investment” and we can very well expect a sizeable share of Android flagships running on the Dimensity 9000. MediaTek suggests the Dimensity 9000 is only “the first in a series of flagship chips,” painting the possibility of a bright future for the chipmaker.