When a massive star runs out of fuel and approaches the end of its life, it explodes in a huge outpouring of energy called a supernova. These events can be so bright that they outshine entire galaxies, but they don’t last for long — just the blink of an eye, in cosmic terms. It’s hard to capture the sudden brightness and fast dimming of a supernova event, because they are difficult to predict, but the Hubble Space Telescope recently managed to capture three different moments of a supernova in a single image.
“It is quite rare that a supernova can be detected at a very early stage, because that stage is really short,” said Wenlei Chen, an author of the paper, in a statement. “It only lasts for hours to a few days, and it can be easily missed even for a nearby detection. In the same exposure, we are able to see a sequence of the images—like multiple faces of a supernova.”
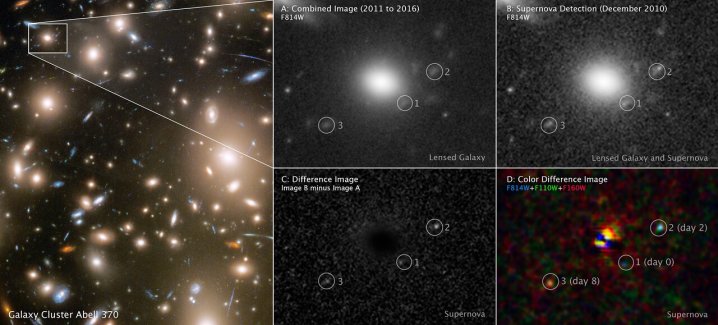
It was possible to see three different points in time due to a phenomenon called gravitational lensing, in which a massive object comes between us and the object being observed. If the intermediate object is massive enough, its gravity warps space, changing the view of the object behind it. That background object can appear brighter when the intermediate object acts like a magnifying glass, and it can appear at a different point in space when its light has been bent. In this case, the light from the supernova was bent along three different paths of different lengths, so the light arrived at Hubble showing three different instances.
The supernova is an extremely distant one, meaning it is ancient — it is estimated that it occurred 11 billion years ago, which is close to the start of the universe 13.8 billion years ago. This is one of the earliest supernovae observed in such detail, and because of the three different time points captured in the image, researchers were able to measure the star’s size. The star is estimated to be around 500 times larger than the sun, a type of star called a red supergiant.
The research is published in the journal Nature.



