You can reset your BIOS in a few different ways, but they all have the same effect: They set all the BIOS settings back to their factory defaults. That means it resets any overclocks you enabled -- including EXPO and XMP profiles -- turns off any features you've enabled by hand, and even defaults the time and date.
Getting the motherboard back to its factory settings can be a great way to fix common boot problems or undo any changes you wish you hadn't made. Here's how to reset your BIOS.
Note: Although technically modern PCs and laptops tend to have a UEFI rather than a traditional BIOS, we'll be using the terms interchangeably throughout this article.
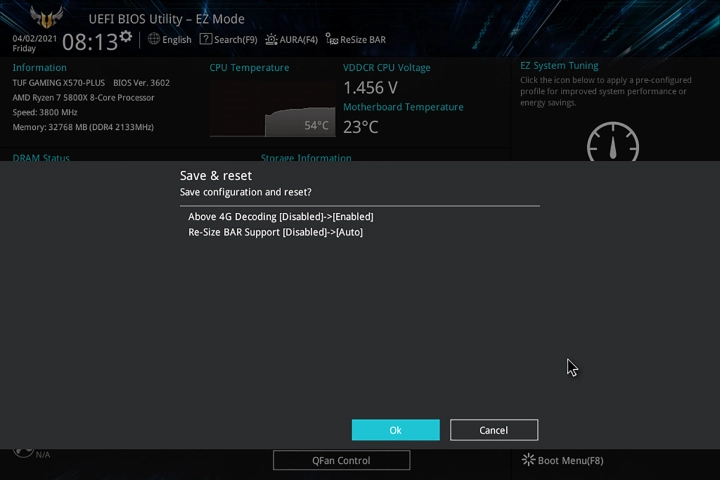
Reset your BIOS in the BIOS
Every BIOS is different, but each comes with a command for resetting the BIOS. It can be called "BIOS Reset," or "Factory Defaults," or "Default BIOS," or a range of other terms, but it's all the same.
Step 1: Reboot your PC or start it up if it was already off, then select your system's specific key for entering the BIOS. It's probablyDelete or F2, but it could be a range of other function buttons depending on your PC or motherboard manufacturer.
For more help on accessing the BIOS, read our guide on how to use the BIOS.
Step 2: Once you're in the BIOS, look at the bottom or right-hand-side of the screen. You should see a key for the commands you can do. They'll tell you which key to select to reset the BIOS to defaults.
Alternatively, look in your motherboard's manual, or check out your system manufacturer's website for instructions on which key to press.
Step 3: Press the key. It may show you a list of changes made. Don't be intimidated -- resetting to defaults can change a lot of settings. If you feel you might want those settings later, see if there's a way to save them first.
When prompted, reboot your PC. If it doesn't prompt you, press the command for saving settings, then confirm to restart. The BIOS should now be reset.
Reset your BIOS using the reset switch
Many modern and high-end motherboards have a BIOS reset switch or button located somewhere on the board. This can be on the back I/O panel, or on the actual motherboard itself, requiring you to open the case to press it.
In any case, if your motherboard has this button, find it using your manual, the manufacturer's website, or just by looking for it -- it should be adequately labeled. Once you've found it, turn your PC off and press and hold the button for a few seconds. Ideally, check the manual or your motherboard manufacturer's website to confirm the precise amount of time you need to hold the button down, but it should be relatively self-explanatory.
Once you've done that, boot your PC up and you should find the BIOS reset.

Reset your BIOS by removing the CMOS battery
The CMOS battery is the small, button/cell battery that sits on your PC's motherboard that powers the BIOS when the system is turned off. This is what allows it to retain the data without the main power supply. You can use it to reset your BIOS, too.
Step 1: Turn your PC or laptop off, and remove the power cable and/or battery, if possible. Then open up the case so you can access the motherboard.
Note: In laptops, this may require removing a lot of screws and other hardware, so only proceed if you're certain and don't mind invalidating the warranty.
Step 2: Locate the battery. It may be located under a graphics card or behind a heat sink. It's usually roughly in the center of the motherboard, but can be located just about anywhere. Check the manual if you can't find it.
Step 3: Remove the battery by pressing the small retaining pin inside the battery holster.
Step 4: Press and hold your PC or laptop power button for 30 seconds. This will drain any remaining power out of the system's capacitors and ensure it has no power at all.
Step 5: Replace the battery and any other components you removed. Replace the side panel and plug the power cable back in.
Step 6: Boot your PC or laptop. The BIOS should now be reset.