Developing self-driving cars is about more than teaching computers when to accelerate or brake. Autonomous driving systems need to be programmed with an untold number of behavioral cues that human drivers take for granted. General Motors-owned Cruise believes the key to making its cars better drivers is by creating better digital maps to guide them. Here’s how Cruise does that.
Some companies buy maps from third-party suppliers, but Cruise chose to develop all of its maps in-house. This gives Cruise complete control, and makes it easier to keep the maps up to date and implement changes, Erin Antcliffe, Cruise’s senior project manager for mapping, wrote in a blog post.
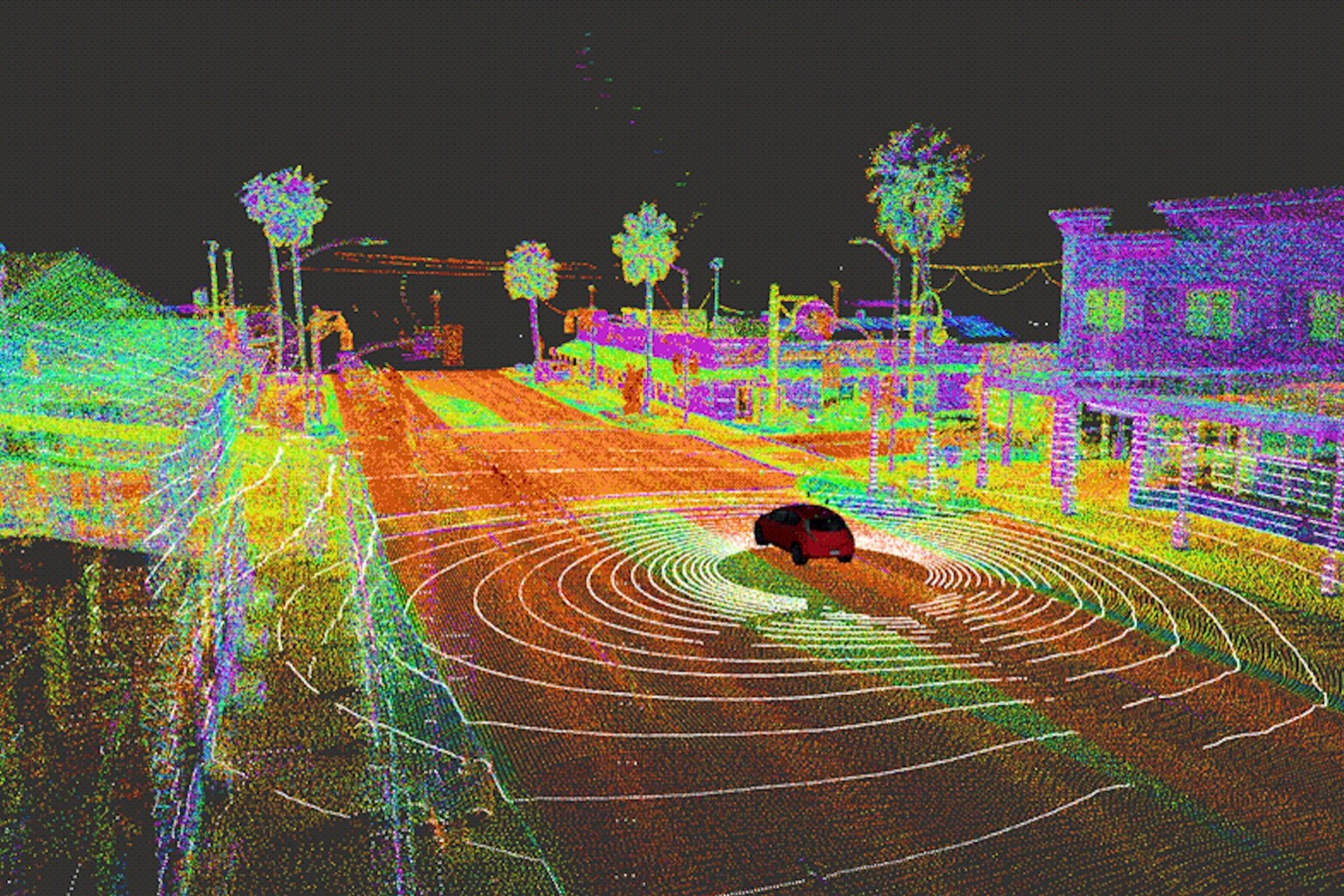
Self-driving cars use maps for the same reason humans do — to figure out where they are. In major cities like San Francisco, where Cruise tests prototype autonomous cars on public streets, tall buildings can block GPS signals, Antcliffe noted. Cruise’s maps also contain information like the boundaries of lanes, and the locations of traffic lights and curbs.
When a car drives down a street, it uses lidar to compare the surrounding environment to a map, allowing it to determine its location down to the centimeter, Antcliffe said. Putting more information onto maps frees up processing power for maneuvers, and gives the car the ability to precisely position itself, she added. That makes it easier for cars to deal with the unpredictable actions of other vehicles, as well as cyclists and pedestrians, on crowded city streets.
That data is only useful if it is accurate, though. Without going into much detail, Antcliffe said Cruise has the ability to quickly update its maps to account for changes such as construction or the addition of new bike lanes. Antcliffe called this a “competitive advantage.”
Map development goes hand in hand with the development of self-driving cars themselves, Antcliffe said. Just like human drivers, self-driving cars perform better when they’re more familiar with the road environment. Cruise is able to encode that familiarity into its maps, adding information based on previous experience in a given area. Multiple versions of a specific map feature can be tested at once, and the one that works best can be quickly applied across Cruise’s autonomous fleet.
Cruise believes better maps will give it an advantage in the race to commercialize self-driving cars, but those plans recently hit a roadblock. Cruise parent GM initially wanted to launch a pilot ridesharing service in 2019, but Cruise has said it cannot meet that deadline. Meanwhile, Waymo has launched a small-scale commercial ridesharing service in Arizona, and other companies are giving rides to the public as part of pilot programs.




