Holden said Los Angeles will be the third city Uber plans to use as a test site for its flying taxi project “Elevate” by 2020. Dallas and Dubai were the first two cities added as initial test sites for Uber’s flying taxi initiative in April. Holden also revealed Uber signed a Space Act Agreement with NASA in an effort to create a custom air traffic control system that would manage Uber’s fleet of low-flying aircrafts.
“[Los Angeles is] one of the most congested cities in the world today,” Holden said. “They essentially have no mass transit infrastructure. This type of approach allows us to very inexpensively deploy a mass transit method that actually doesn’t make traffic worse.”
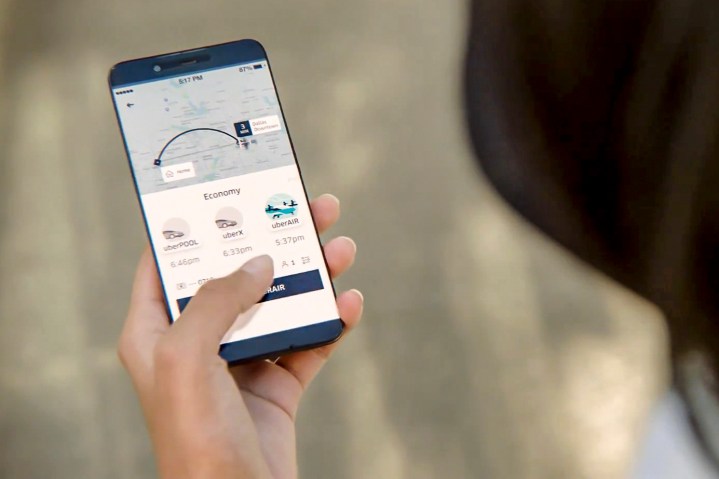
Uber also unveiled a concept video of how hailing a flying taxi would work. In a promotional video, a woman uses the Uber app to hail a flight on UberAir. Afterward, she enters a building and takes an elevator to the top floor labeled “Uber Skyport.” Once she’s reached the Skyport floor, she scans a QR code from her digital boarding pass on her phone to gain entry. She is accompanied by three other people in the aircraft with and there is an overhead display showing the flight path, elevation, speed, and arrival time.
Even if catching a flight becomes as easy as hailing a taxi, the UberAir fleet won’t be considered flying cars. Uber says the aircraft will be electric vertical take-off and landing vehicles (EVTOL). The EVTOL aircraft will possibly be autonomous and use distributed electric propulsion which will allow the vehicles to fly you around while making very little noise. But, these EVTOLs never hit the road, nor do they have an essential component of anything related to a car.
The tagline at the end of the promotion video reads “closer than you think.” With companies such as Air Bus and Boeing working on their own flying car fleet, Uber’s promise may be truer than you may believe.


