Intel is the newest player in the GPU market now that the company has finally launched its Arc Alchemist GPUs. Since these are first-generation products from a company that has almost no experience in making desktop-grade graphics, you might wonder if GPUs like the Arc A770 and A750 support modern features like ray tracing.
Intel Arc does in fact support ray tracing, just like AMD and Nvidia does, and the performance might even surprise you.
Does ray tracing work on Intel Arc?

You might recall that in 2018, when Nvidia first introduced its Turing architecture with ray tracing capability, not all Turing GPUs actually had ray tracing support. All RTX 20-series cards had ray tracing, but not the lower-end to midrange GTX 16-series, which used significantly less complex silicon.
Given that Arc is both Intel’s first attempt at gaming GPUs for the desktop and also Intel’s first ray tracing-capable GPU, you might wonder if only the higher-end Arc cards have ray tracing support. In fact, all Arc GPUs have the hardware necessary for ray tracing, even the lowest-end A310.
On a software level, Arc supports ray tracing in DirectX 12 and Vulkan titles, which represents almost all games that have ray tracing. This puts Arc on equal footing with AMD and Nvidia when it comes to software compatibility.
Intel Arc Alchemist ray tracing benchmarks
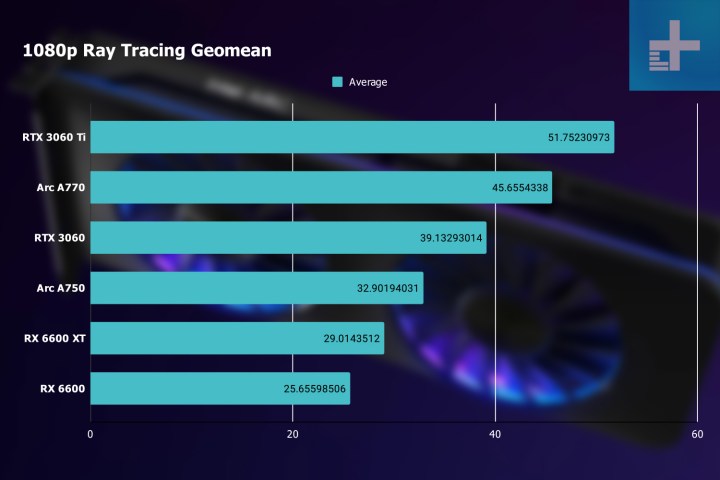
Of course, being able to turn on ray tracing doesn’t mean much if the performance is bad. Again, this is a first-generation product for Intel in multiple aspects, and you’d be justified in being a bit skeptical about whether or not Arc can really perform. Well, as you can see in the above chart from our Arc A770 and A750 review, these midrange cards are actually quite good at ray tracing.
On average, the A770 is about 18% faster than the RTX 3060 and just 12% slower than the RTX 3060 Ti. AMD’s midrange GPUs can’t really hold a candle to Intel or Nvidia, which means that Arc is in at least second place in the ray tracing game.

It is important to point out that ray tracing is extremely resource intensive and on midrange GPUs, the frame rate can be so low that there’s no point in enabling it.
In Cyberpunk 2077, which we tested at 1080p and with ray tracing set to Ultra, the performance wasn’t very good on Intel Arc or any other GPU, with only the RTX 3060 Ti achieving above 30 frames per second (fps). But that’s not the case for other games.
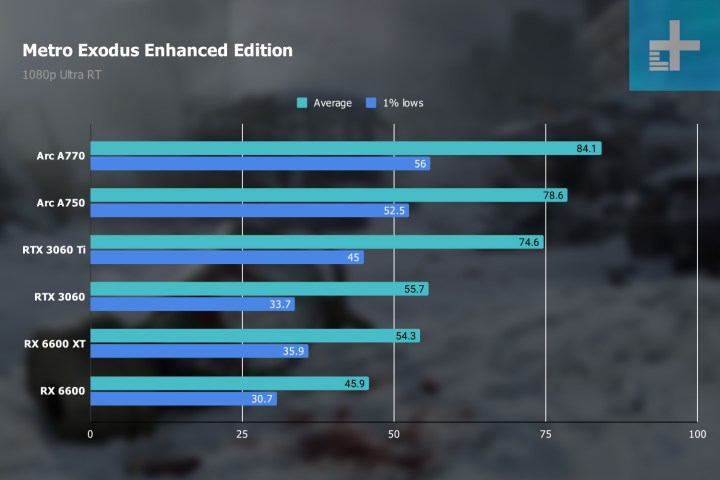
In Metro Exodus, which we tested with similar settings, all GPUs were able to hit playable frame rates. The A770 and A750 even lead in this benchmark, beating the RTX 3060 Ti and RTX 3060 by a significant margin. None of these GPUs (Intel, AMD, or Nvidia) are for gamers wanting to enable ray tracing in every single game possible, but they do support ray tracing and can do it well enough in some games, which is better than nothing.
We haven’t tested lower-end Arc GPUs like the A380 or the A310, but based on the spec sheet alone, we can probably guess that they have very poor ray tracing performance. The A770 has 32 ray tracing units (or RTUs), while the A380 has eight and the A310 has just six, which means the A380 has a fourth of the RTUs the A770 has.
Some early reviews of the Arc A380 found that the GPU could just barely reach 30 fps in a few titles at 1080p, which is not great to say the least. While ray tracing is technically supported across the entire stack, that support is of questionable use depending on the performance. The A770 and A750 at least have some reason to support ray tracing, however.




