A gaming GPU from Intel? It may sound like blasphemy, but the new Arc chip line proves otherwise. In fact, we’re seriously impressed with Intel’s gaming graphic cards, calling them “the right GPU at the right time” with their excellent 1440p performance, competitive ray tracing, and pricing that’s somehow relatively reasonable. They even – dare we say it – work quite well with AMD Ryzen processors.
But there’s a small catch: You’ll need to make sure that Resizable BAR is turned on if you want to get full performance. In fact, Intel has bluntly stated that Arc GPUS must use Resizable BAR (which Intel shortens to ReBAR) for proper gaming optimization. If you're a new owner of an Arc GPU, here's how to use ReBAR.
What is Resizable BAR?
Resizable BAR stands for Resizable Base Address Registers. It’s an optimization technology that allows processors more effective access to VRAM memory on graphics cards. That in turn leads to performance upgrades for certain kinds of games, because it reduces CPU bottlenecking. It’s available as Resizable BAR on the latest Nvidia cards, as Smart Access Memory for newer AMD GPUs, and now as ReBAR for Intel’s Arc line.
We have a more complete guide to what ReBAR is and how it actually works, but the bottom line is that it can make certain games, especially games that demand a lot of memory, run better on your gaming rig. It can be particularly noticeable on loading screens, on changing scenes, and in similar situations.
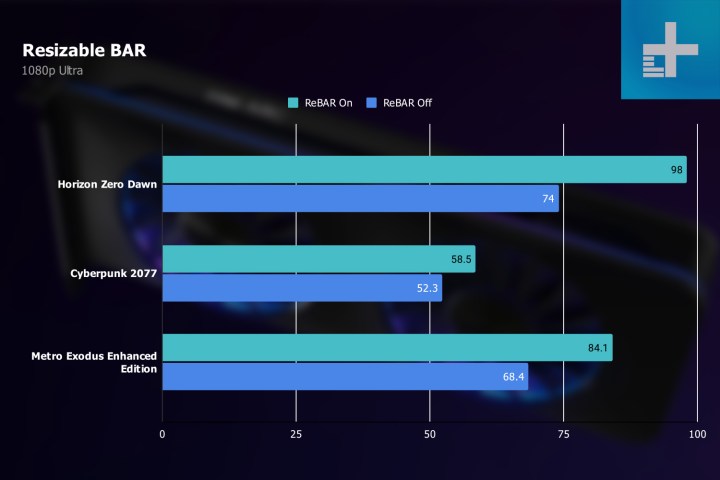
Along with Intel's own suggested use of ReBAR, our reviews of Arc cards also found enough performance improvements to consider the setting essential.
How to enable ReBAR on Intel Arc GPUs
Step 1: Check that you have a supported processor. Only certain processors can actually use Resizable BAR features. The good news is that many chips from the last few years are compatible with it. That includes most Intel 10th-generation chips or newer, as well as most Ryzen 3000 (excluding 3000G), 5000, and 7000 chips. Check your specific processor for compatibility if you aren’t sure.
Note that motherboards will need a full-size PCI Express 3.0 or newer x16 slot for ReBAR. This isn’t as much of a concern if you already have a compatible processor, but you may want to check your connections if you have a particularly unique setup.
Step 2: If you haven’t already done so, install the Intel Arc GPU and download any necessary drivers. Intel’s Control software may give you notifications regarding Resizable BAR support at this time, which can be a helpful confirmation of your status. Once you are sure the GPU is functioning correctly, reboot your PC and press the Delete key during startup to enter the BIOS/UEFI.
The Delete key will typically get you to UEFI, but sometimes it’s the Esc key or a Function key like F1. Check your PC model if nothing seems to be working. Windows 10 and 11 also have an Advanced startup option in Update & security that you can use to directly boot into UEFI if necessary.
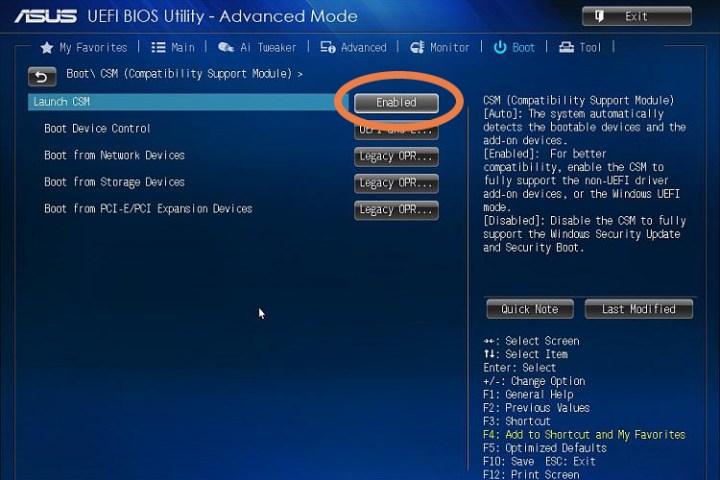
Step 3: Note that you must be in the UEFI version of your settings, not any BIOS emulation modes. That means that you may have to disable settings like CSM (Compatibility Support Module) or Legacy Mode. Anything that makes UEFI look like the older BIOS settings should be turned off. You may also need to enable a UEFI Boot Mode if it isn’t already on. Do this now if necessary.
Step 4: Here’s where things start to vary a lot based on the components you are using. Different system manufacturers will use different wording for the same thing and will bury options in different menus. That may mean doing some searching, or checking your motherboard manual. Ultimately, though, you're looking for these two important settings:
First, turn on Above 4G decoding if it’s available. You should see an option to Enable, toggle on, or switch to Auto mode, any of which should do the trick. If you don’t see an option for Above 4G Decoding, continue to the next step. If you do, enable it, reboot, and head back into UEFI before continuing.

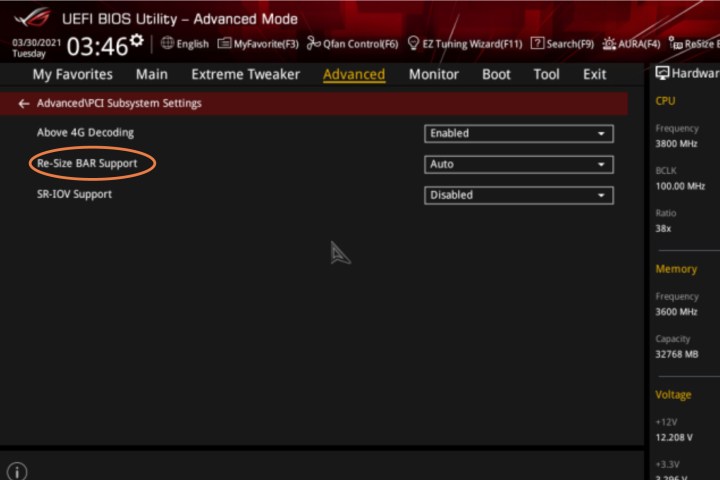
Step 5: Now, look for a setting called Re-Size BAR Support. It might also be called Smart Access Memory on Ryzen machines, or sometimes Clever Access Memory. Enable it. Our example shows how it looks on an Asus motherboard, but yours may look differently depending on your motherboard and UEFI version.
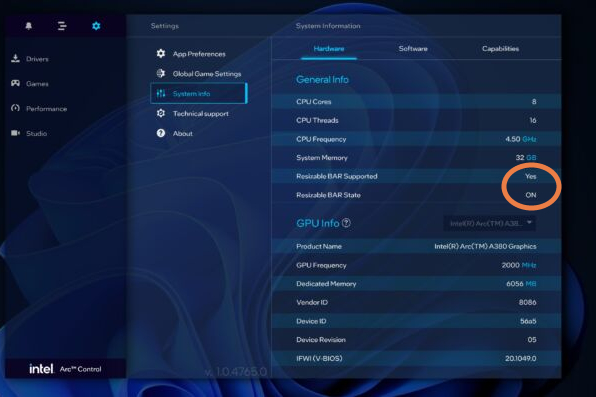
Step 6: Now reboot out of UEFI. If you open the Intel Arc Control app, it will typically confirm that ReBAR is working, and you shouldn’t need to adjust any additional settings this time. In Control settings, you can go to System info and look at General info to confirm that Resizable BAR is supported and on. Just make sure that your ARC GPU gets any available updates, and game on!