This is big news, as a good chunk of the general consumer market relies on laptops and tablet/laptop hybrids. Battery life extension is one of the hottest topics in the mobile market today as consumers surf the Internet in their cars, on the plane, and even at the park. Hardware and software developers are struggling to push those power savings to the max, and Opera seems to be latest to jump on that trend.
Opera’s Pawel Miniewicz claimed in a recent blog that the desktop version of the Opera browser can extend the user’s battery life by up to 50-percent while browsing thanks to the new power saving mode when compared to other browsers on the market like Google Chrome. This is a bold claim, but Miniewicz backs it up with a few numbers and a list of hardware that was used during a recent test.
Opera used two platforms in its testing process: a Lenovo ThinkPad X250 with an Intel Core i7-5600U processor and 16GB of memory, and a Dell XPS 13 with 16GB of memory. Both ran a copy of Microsoft’s 64-bit version of Windows 10, and both were set at a high performance power mode. On the software front, the company used Selenium WebDriver. It loaded 11 popular websites in separate tabs, which in turn were scrolled five times. The tests were conducted until the laptops ran out of battery juice.
According to a provided chart, the laptops lasted one hour and fifty-four minutes when using Google Chrome, and one hour and fifty-eight minutes when using Opera with the power saving mode turned off. However, when the power saving mode was switched on, the battery lasted for two hours and fifty-six minutes, a 49 percent battery life increase. Miniewicz noted that Opera’s ad blocker was also loaded during the testing process.
To keep the Opera browser from eating up the laptop’s battery, the company made a few “under the hood” adjustments. For starters, the company managed to reduce the activity in the background tabs. They also figured out how to wake the CPU less often by optimizing the scheduling of JavaScript timers. The overall framerate was reduced to 30 frames per second, and browser theme animations are paused when the power saving mode is activated. Unused plugins are also automatically paused.
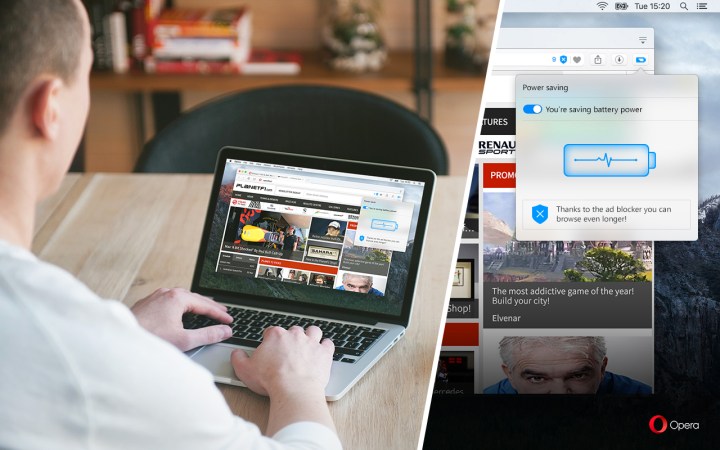
Opera users can enable the power saving mode by clicking on the battery icon seated next to the search and address field within the browser. This icon will automatically appear when the laptop’s power cable is unplugged. Opera will also suggest switching over to power saving mode when the laptop’s battery reaches a 20-percent capacity.
In addition to the new power saving mode, the browser’s VPN experience received an upgrade and is now part of the private browsing mode. For example, the company disabled WebRTC support when the VPN mode is enabled because web pages could see the user’s IP address when establishing a WebRTC connection. A VPN badge now appears in a private window as well.
The new features listed in Miniewicz’s blog post can be found in the developer channel build of Opera for computers. This version is updated a few times per week, so expect it to be somewhat less stable than the version released to the general public.


