Thunderbolt 4 is the latest generation of Intel’s Thunderbolt technology, and though it doesn’t revolutionize the standard, it does shore it up in ways that make it far more of a high-performance guarantee than competing standards like USB4. However, the tech may not be all about raising the minimums. Intel has demonstrated Thunderbolt as being capable of far greater performance; it just hasn’t implemented it yet.
Here’s what you need to know about Thunderbolt 4 to make the most of this high-speed and high-performance connection standard.
Availability

Intel officially announced Thunderbolt 4 at CES 2020, with the first supporting chips, Intel’s own Tiger Lake mobile CPUs, launching at the end of that year. Thunderbolt 4 saw much wider availability in 2021 with the launch of third-party Thunderbolt 4 cables, and today Thunderbolt 4 ports can be found in all the latest generations of laptops, including Apple’s MacBook Pros.
Thunderbolt 4 cables are available from a range of brands and are comparably priced to Thunderbolt 3 and USB4 cables.
Performance
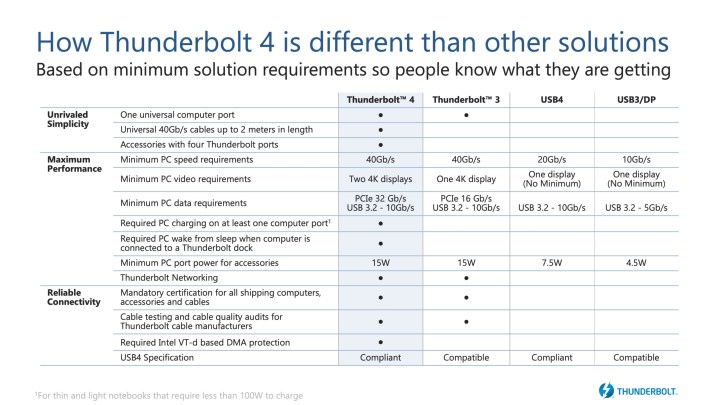
As far as speed goes, Thunderbolt 4 is not explicitly faster than Thunderbolt 3. Both generations of Thunderbolt can have a maximum capable throughput of 40 Gbps. However, where Thunderbolt 3 has a minimum guaranteed data rate of just 10 Gbps, Thunderbolt 4 has a minimum data requirement of 32Gbps, with an additional 10 Gbps available for PCIExpress video transmission using DisplayPort alt mode.
This means that while there are Thunderbolt 3 cables that can offer the same performance as Thunderbolt 4, most won’t. If you want a greater performance guarantee, Thunderbolt 4 is the way to go. That’s especially true when you consider that Intel has shown Thunderbolt cables transmitting at up to 80Gbps, though it’s not yet clear if that’s for a future Thunderbolt 4 cable, or an expected Thunderbolt 5 generation of the technology.
That extra PCIExpress bandwidth means that Thunderbolt 4 can also support multiple monitors in a daisy-chain configuration, making it a great solution for external monitors outputting from laptops.
Features
Thunderbolt is a standard jam-packed with features, from enabling external graphics cards to providing Ethernet network access, many designed to continue differentiating Thunderbolt from the USB standard. We already mentioned the new 32Gbps SSD connection speed, but for a device to be certified for Thunderbolt 4, it must also include key features like:
- Double minimum video data requirements compared to Thunderbolt 3. This will allow support for two 4k displays or an 8k display if necessary.
- Support for docks with up to four Thunderbolt 4 ports, more than Thunderbolt 3 requires.
- Wake features that allow you to immediately wake the computer at a touch of the keyboard or mouse when connected to a Thunderbolt dock (when this didn’t work with Thunderbolt 3 computer, it quickly became very annoying for frequent users and was a long-awaited fix).
- Thunderbolt 4 can provide up to 100W of charging for mobile devices, making it a great all-in-one cable for providing, data and power to a laptop, whilst sending display data to an external monitor.
Thunderbolt 4 is also backwards compatible with all other forms of USB-C. That includes USB-C 3.2 2×2, USB4, and Thunderbolt 3.
FAQ
Is Thunderbolt 4 different from USB-C?
Thunderbolt 4 uses the USB-C connection type, just like Thunderbolt 3 and USB4. However, it is based on the Thunderbolt protocol, which offers greater performance and feature guarantees than USB4.
Which is faster, Thunderbolt 4 or USB4?
Thunderbolt 4 has a greater performance guarantee, with its minimum of 40 Gbps total bandwidth. In comparison, while USB4 can reach that sort of bandwidth, it is only mandated to support 10 Gbps. New standards for USB4 suggest it could reach 80 Gbps — in a similar manner to Intel’s 80 Gbps Thunderbolt demonstration.



