Intel Optane memory might sound like a new standard of RAM, but it has more in common with modern storage solutions like solid state drives (SSDs). Yet it’s designed to supplant SSDs in some ways — and augment them in others. In short, Intel Optane provides much faster read and write speeds than even the fastest SSD can match without RAM’s constant power requirement.
More than a year on from the technology’s debut though, it hasn’t been quite as impactful as some might have expected. Some of that surely has to do with some confusion as to what exactly Intel Optane does and where you can find it — so let’s clear some things up.
Where can you find it?
Today there are a number of Intel Optane-equipped SSDs available. The first to appear was Intel’s DC 4800X SSD. That name isn’t catchy, because it doesn’t have to be. It’s an enterprise product, where potential buyers are far more concerned with dollars per performance than branding or aesthetics.
There are more options for the average person, too. Intel launched 60GB and 120GB Optane SSDs earlier this year, priced at $130 and $200 respectively. Using Intel’s 3D XPoint memory modules, they offered high-speed read and write rates that rival strong M.2 and NVMe SSDs from more traditional SSD manufacturers, but only in small capacities. Their small form-factor makes them viable options for inclusion in miniature PC builds and laptops, though their higher-than-average cost per gigabyte still makes them uncommon in pre-built systems.
Intel followed up that launch with the much more performance-focused Intel Optane 900P and 905P range of SSDs later in the year and eventually expanded size options for the latter range in September. Today the PCIe Optane SSDs are available in 500GB, 1TB, and 1.5TB sizes, with the 905P range offering sequential read and write speeds as high as 2,600MB/sec and 2,200MB/sec.
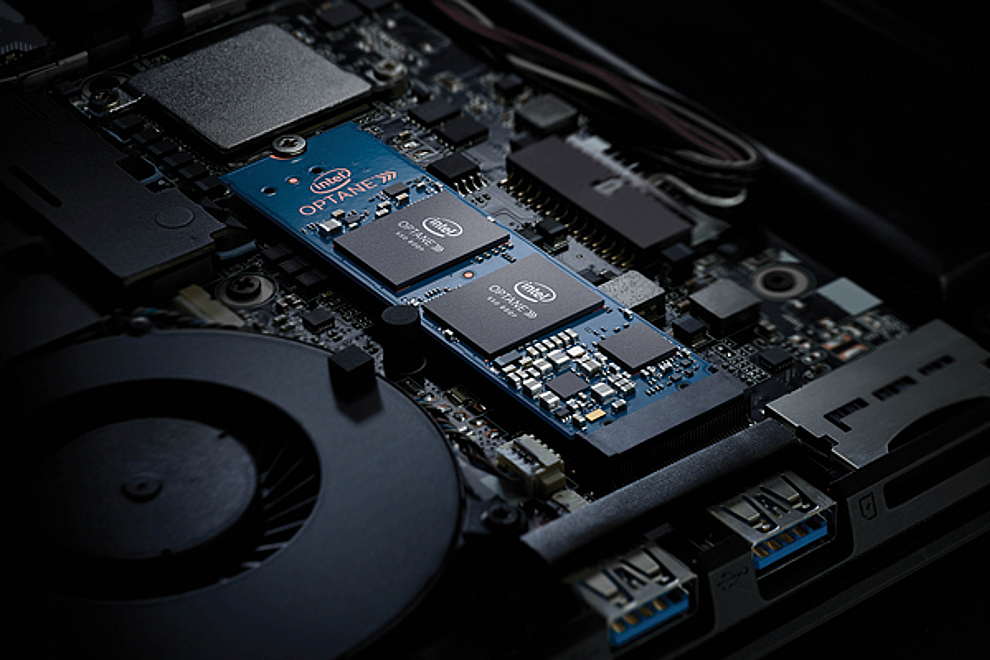
At the other end of the spectrum, Intel Optane Memory attempts something much more like the enterprise-focused DC 4800X. The 16GB and 32GB devices are designed to act like caching drives, automatically keeping the most commonly used files on that drive, giving old HDDs a boost of speed. We spent some time with those drives, and though enthusiasts will want to opt for dedicated SSDs, systems like the Acer Aspire 5 really benefited from the fast caching abilities of Optane memory. Even impressive all-in-one systems like the HP Envy 27 have taken advantage of it.
The big reason manufacturers (and hence, the average person) can benefit from Optane is cost. A 16GB Optane module costs just $34 to consumers — and likely far less when purchased in bulk by system builders. That’s far cheaper than trying to pack in a middling-size SSD that only offers greater performance up to its own capacity. An Optane module can boost a far greater amount of data than its modest size might suggest, switching out what it stores to whatever is accessed most often.
Under the hood
So, what exactly is Intel Optane? We aren’t quite sure, because Intel won’t tell us. The company has even responded to questions of the underlying materials with cagey answers and “no comments,” which leaves us wondering what sort of digital witchcraft powers this fast, non-volatile storage.
What we do know is rather basic. Optane is based on a previously announced Intel and Micron project knows as 3D XPoint, and the details quickly grow complex from there. In essence, it allows for greater speeds by changing the resistance across bits in large batches, rather than one at a time, and packs in more of that memory by stacking the arrays in rows, which are turned 90 degrees on each layer. The image below lays out an example of how this looks at a microscopic level.

Don’t confuse 3D XPoint with 3D NAND, however, which is simply flash memory stacked in more efficient configurations. Instead, 3D XPoint operates on (possibly) different materials, with proprietary forms of data storage and transfer, the details of which are a closely guarded secret.
It also isn’t the end of the story, because 3D XPoint is just the storage type, while Optane is a collection of first-party Intel hardware, firmware, and software that turns that mysterious chunk of whatever-it-is into a device that’s usable in a myriad of situations. Intel has quickly expanded its range of Intel Optane products from some simple caching hardware, to dedicated storage drives which are getting bigger and more affordable all the time.



