The Windows 11 launch is right around the corner. Devices featuring the new operating system are set to launch on October 5, and Microsoft is offering Insiders the opportunity to download and use the OS now.
If you have an unsupported processor, though, you’ll need to sign a waiver accepting any possible “damages” to your PC — but the real risk is the lack of updates.
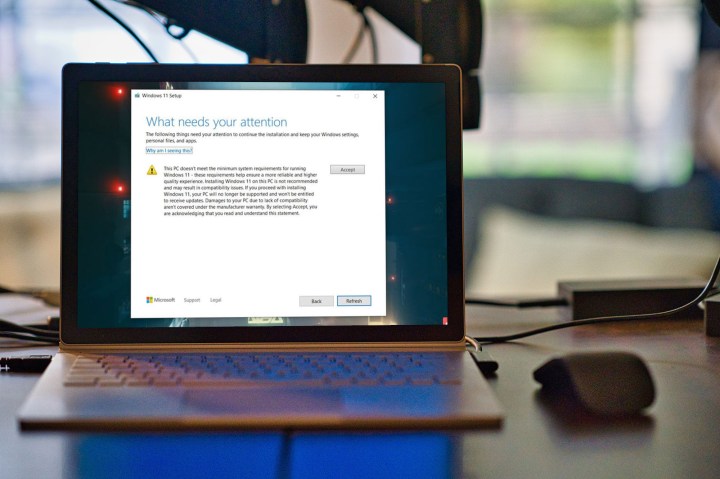
Let us explain. In August, Microsoft announced that it would let users with unsupported processors install Windows 11 manually. At the time, the company implied that users who went this route wouldn’t receive critical driver and security updates. The waiver suggests that this is the case, which poses a far greater risk than whatever “damages” the waiver talks about.
It reads: “If you proceed with installing Windows 11, your PC will no longer be supported and won’t be entitled to receive updates. Damages to your PC due to lack of compatibility aren’t covered under the manufacturer warranty.” After hearing about it, I tried installing Windows 11 on my XPS 15 with its Core i7-7700HQ (which isn’t supported by Windows 11).
You need to be in the Dev channel of Windows Insider to install Windows 11 on unsupported hardware right now. After switching from the Beta channel, I encountered the waiver warning me about damages to my PC.
It makes sense — Microsoft is covering its legal bases, and the disclaimer isn’t buried in a body of legal jargon like it might be elsewhere. The most damaging part of using Windows 11 on unsupported hardware isn’t the hardware, but the fact that it’s not entitled to updates.
Microsoft has reasons for restricting Windows 11 to certain hardware. Newer processors carry better security, including support for firmware TPM, Secure Boot, and virtualization-based security. Microsoft says the combination of these security features can reduce malware by up to 60% based on its testing.
Withholding security updates makes Windows 11 less secure for unsupported hardware.
That’s all good — newer processors are more secure, and Windows 11 is set up to take advantage of the latest security features. The waiver stands by that fact, and it serves as a nice deterrent for anyone — if they exist — who may stumble upon the manual Windows 11 installer without context. It doesn’t explain the update situation, though.
Withholding security updates makes Windows 11 less secure for unsupported hardware. It makes sense that Microsoft doesn’t want to publicize unsupported installs, but it doesn’t make sense to keep driver and security updates from those users.
Presumably, Microsoft will post updated versions of Windows 11 to its official download page. The latest feature builds of Windows 10 have consistently gone up there, and it doesn’t look like Microsoft is changing that for Windows 11. Plus, the Windows 11 installer automatically checks for new updates and features.
Because of that, unsupported PCs may have to go back to this page when there’s an update to reinstall the OS, instead of just getting the release through Windows Update. Or worse, they’ll have to update all of their drivers manually.
We have reached out to Microsoft for clarification on this point, and we’ll update this article when we hear back.
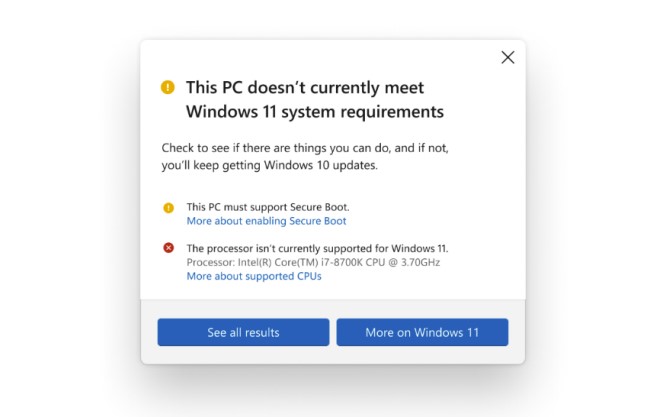
Although it’s easy to poke Microsoft ove the troubles it has had rolling out Windows 11, the company has responded positively to a lot of feedback. The updated PC Health Check app, which tells you if your computer can run Windows 11, now gives detailed compatibility responses. And users with unsupported hardware can install Windows 11 manually, which wasn’t the case when the OS was announced.
Still, looming issues like the TPM and restrictive CPU requirements have barred PCs that are more than a few years old from using Windows 11. Although it’s possible to install the OS manually, the lack of security updates poses a significant hurdle — and Microsoft is acknowledging that through the waiver.



