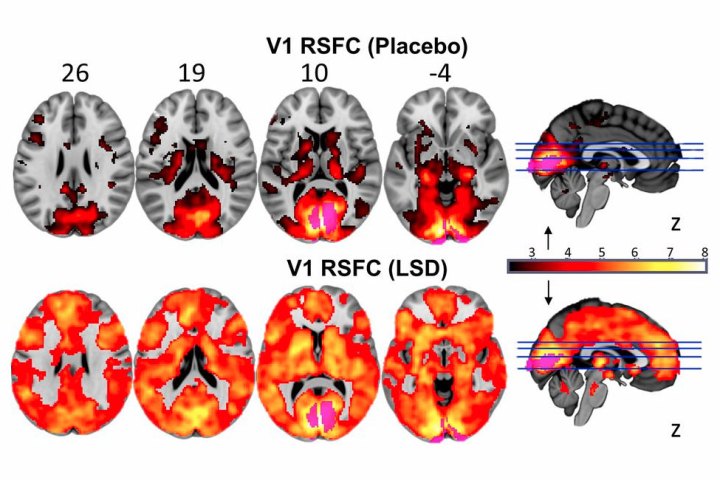
To complete their study, scientists asked 20 healthy volunteers to pay two visits to clinics on different days. On the first day, they were given a “common” oral dose of a 75-microgram LSD injection. On the second day, they received a placebo. Three different brain imaging techniques were then employed to analyze blood flow, brainwaves, and functional connections both within and between brain networks. The results speak for themselves.
The scans clearly indicate the significant hallucinogenic effects LSD has on the brain, lending credence to the notion that tripping on acid tends to allow to people to see sounds and hear color. “Under normal conditions, information from our eyes is processed in a part of the brain at the back of the head called the visual cortex,” the researchers said in a statement. “However, when the volunteers took LSD, many additional brain areas — not just the visual cortex — contributed to visual processing.”
While on the drug, volunteers’ brains were essentially awash with color, suggesting that the entirety of the organ was being used to process information. “We see this explosion of communication,” said Dr. Robin Carhart-Harris, from the Department of Medicine at Imperial, who led the study. “Our results suggest that this effect underlies the profound altered state of consciousness that people often describe during an LSD experience,” he continued. “It is also related to what people sometimes call ‘ego-dissolution,’ which means the normal sense of self is broken down and replaced by a sense of reconnection with themselves, others, and the natural world. This experience is sometimes framed in a religious or spiritual way — and seems to be associated with improvements in well being after the drug’s effects have subsided.”
While LSD was initially developed as a treatment for psychiatric disorders in the early 20th century, the abuse of the drug has quickly turned it into one of the most dangerous substances around. But now that scientists have a clearer picture of what’s going on when LSD is in play, things may change for the better. “For the first time we can really see what’s happening in the brain during the psychedelic state, and can better understand why LSD had such a profound impact on self-awareness in users and on music and art,” said Professor David Nutt, former chairman of the U.K. Advisory Council on the Misuse of Drugs and senior researcher on the study. “This could have great implications for psychiatry, and for helping patients overcome conditions such as depression.”