“This is a touch-sensing technology, similar to what you have with your smartphone screen, but applicable to any surface you can think of,” Professor Chris Harrison, head of Carnegie Mellon’s Future Interfaces Group (FIG), told Digital Trends. “With it you can make tables, walls, furniture, TV remotes — anything you can put paint onto — into a touchpad.”
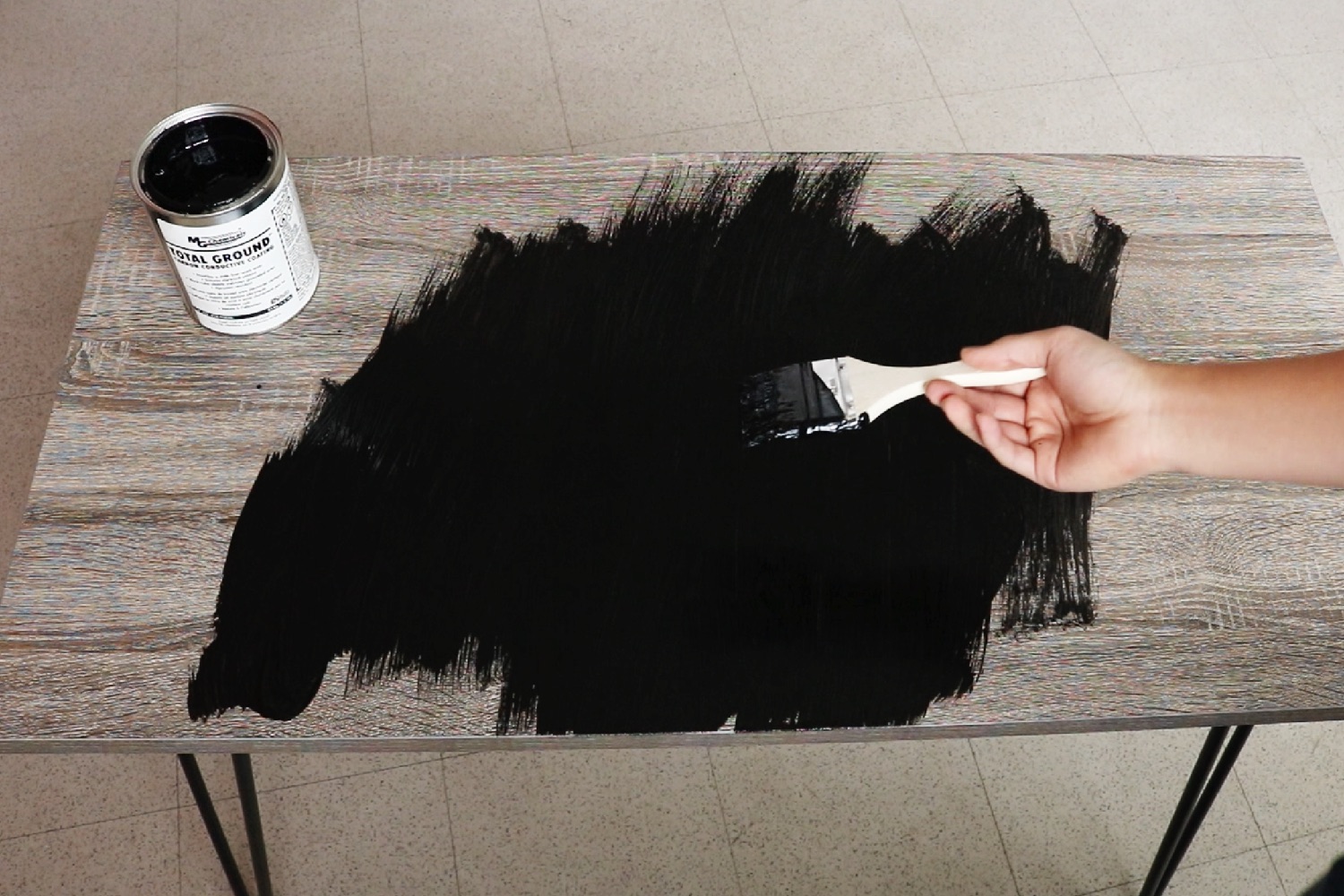
The technology is based around an algorithm that’s able to read a finger press by sensing changes in the flow of electricity over a conductive surface. This concept is called electric field tomography, and involves running small amounts of current through pairs of electrodes and looking for any voltage differences. By attaching electrodes to the periphery of the object covered in Carnegie Mellon’s smart conductive coating, Harrison and colleagues demonstrated that it was possible to sense exactly where a touch had been placed.
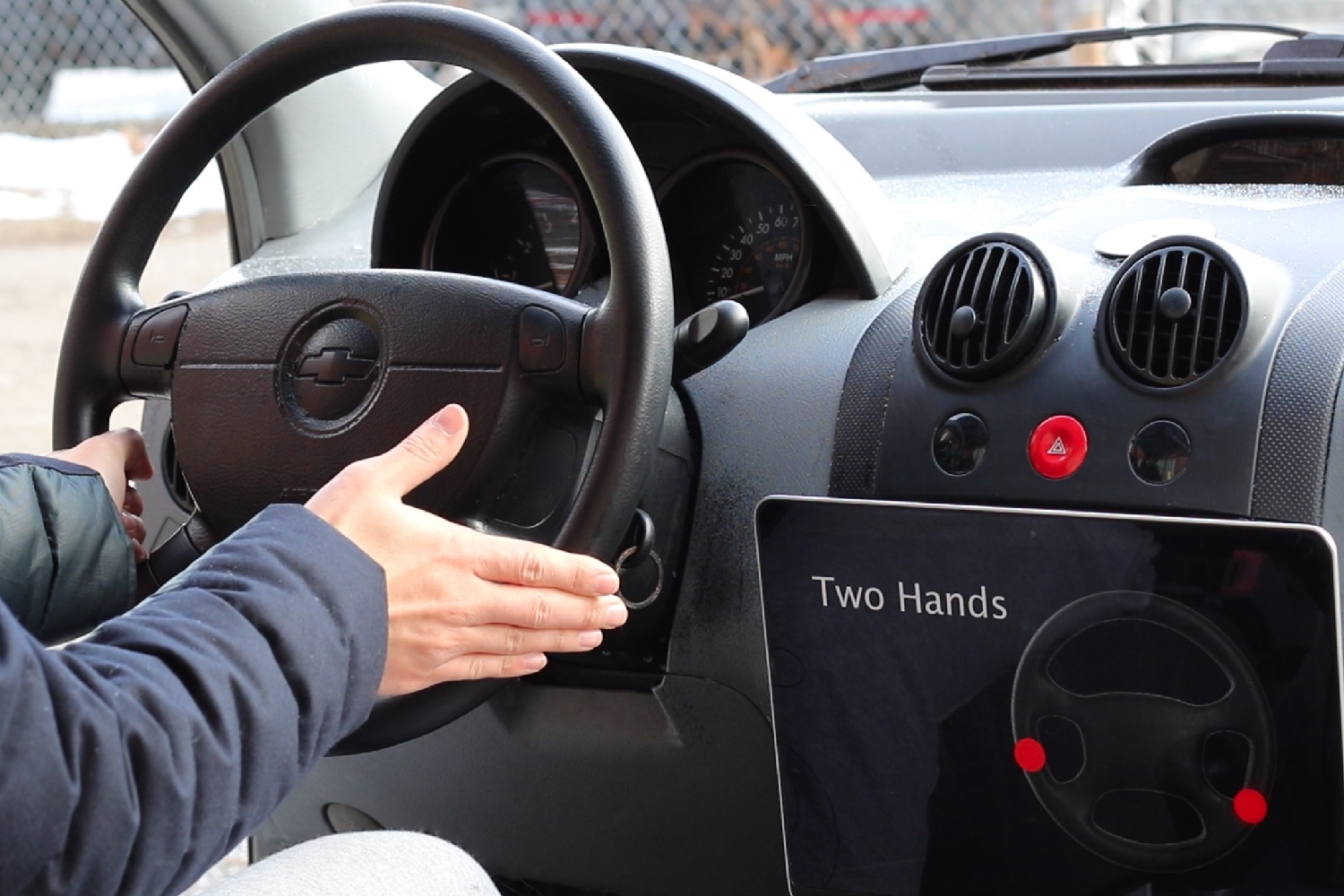
“It’s really exciting to think about the ways companies might apply these sort of finishes to make wholly new forms of interactive goods,” Harrison continued. “For example, you could have a steering wheel that can determine whether or not your hands are placed on it in the right location. Right now, the state-of-the-art tech that we have in cars is a touchscreen display in the Tesla. But imagine being able to make the steering wheel and the entire dash of a car interactive, just by adding an extra coating!”
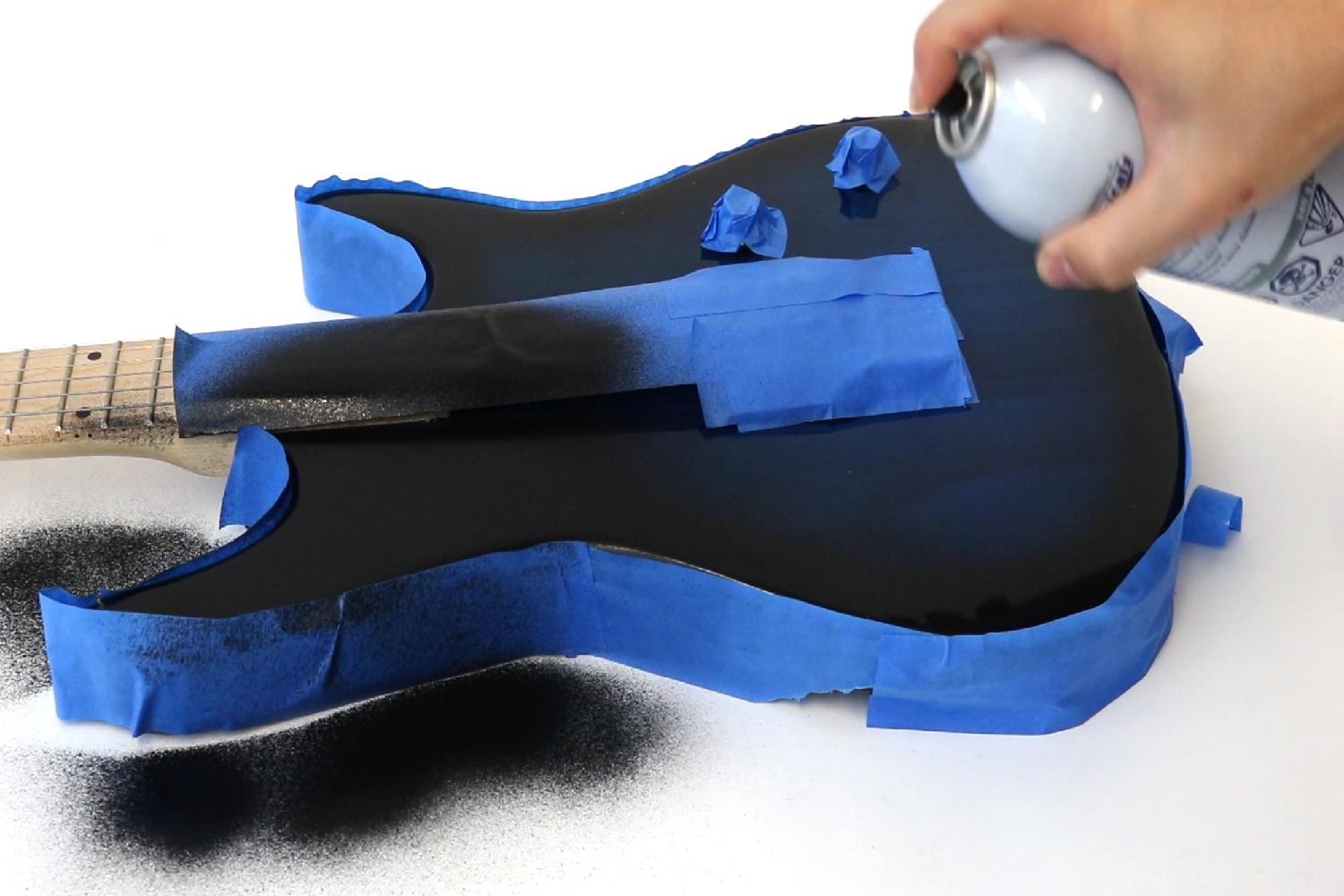
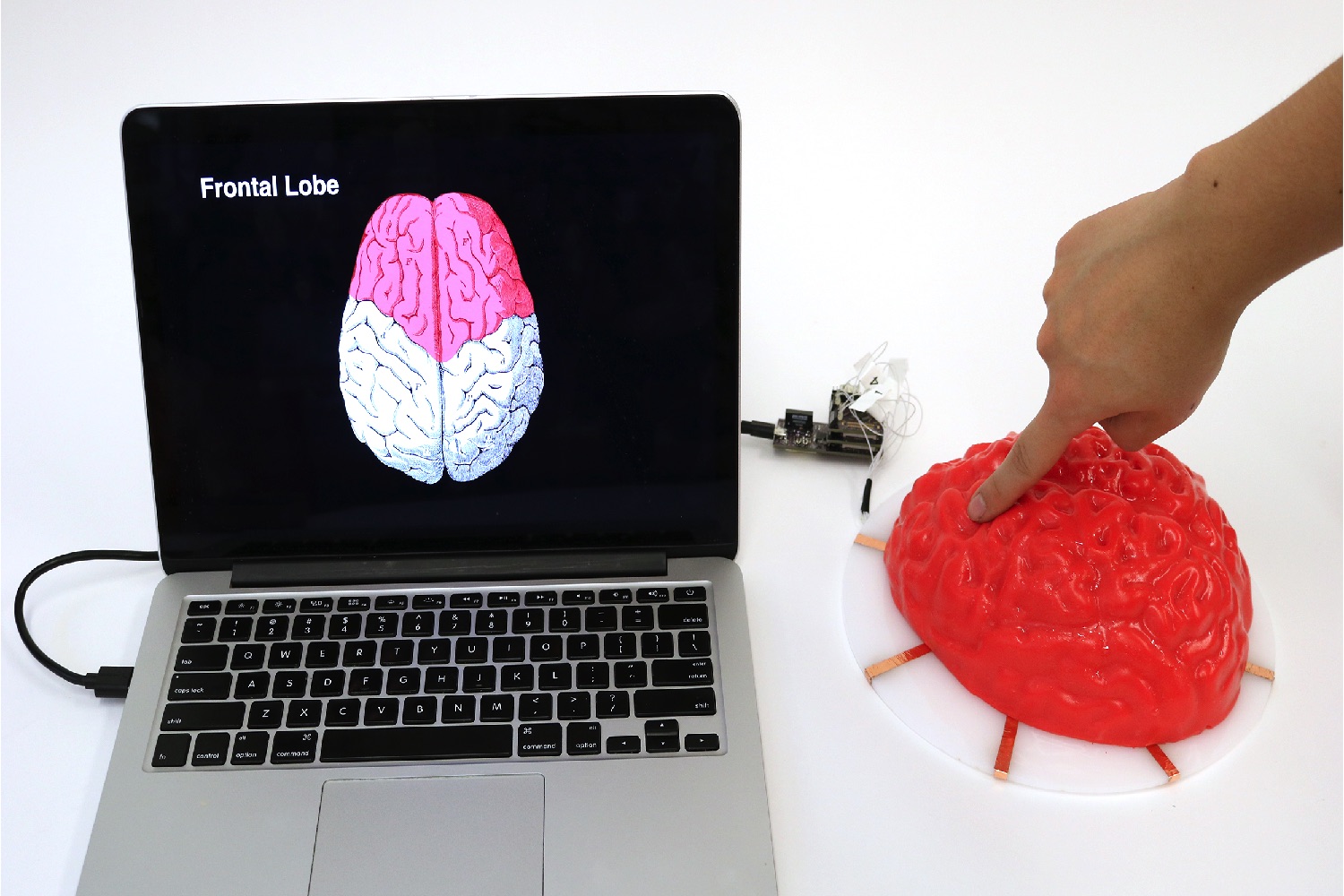
In demos, Electrick was used to add touch-sensing capabilities to objects including (but not limited to) a sheet of drywall, the surface of a guitar, and a Jell-O mold of a brain. All offer unique possibilities in terms of potential applications. For instance, it’s easy to imagine how conductive paint could be applied to a guitar to allow effect pedals to be incorporated directly into its body.
The other big advantage of the system, Harrison noted, is its cost. He describes it as “ridiculously low cost,” and says that adding smart touch-sensitive surfaces to an object works out as, “way under $1 per square foot.”
There are, of course, limitations. Despite being touch-sensitive, the objects don’t include a display, which means the inputs have to be read on another device (like touching the aforementioned Jell-O mold of a brain as a way of controlling a mobile app) or else be used to control relatively simple interactions, like lights switching on or off.
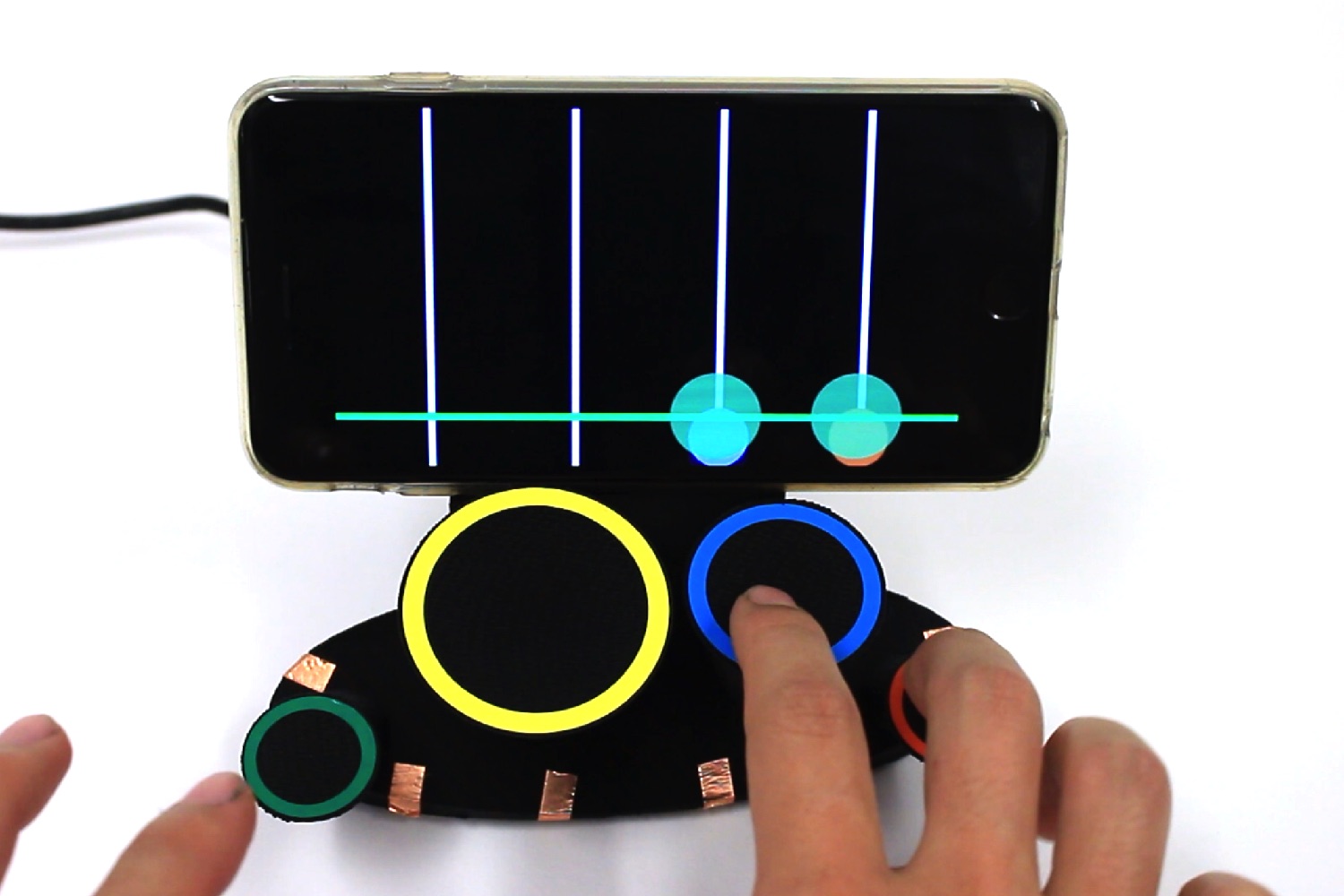
Right now, the system also can’t do multi-touch, referring to the common interaction method on a trackpad or touchscreen in which more than one points of contact with the surface are recognized simultaneously. That could well change in the future, though.
Next up, Harrison said the goal is to further refine the technology. This will include not just further improving the accuracy of the touch-sensing capabilities, but also grappling with questions like how to avoid scenarios involving unwanted accidental touches. After all, it’s one thing to fantasize about a possible Star Trek future in which every surface in our homes is interactive; another to deal with the reality of that scenario, were it to be implemented poorly.
After that, the team’s ambition is then to find a way of getting the Electrick technology out into the real world where it belongs: something Harrison is more than keen to do.
“In our lab we do applied work that’s about attacking real world problems, whether that’s improving people’s lives or simply delighting them with a new experience,” he said. “But at the same time we’re not the commercial arm of a big company, so we’d be looking for partners that could take this technology to the next level.”
The technology was shown off this week by its creators, which included co-authors Yang Zhang and Gierad Laput, at the Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems in Denver. If you’re interested in finding out more, you can check out the full research paper — titled “Electrick: Low-Cost Touch Sensing Using Electric Field Tomography” — here.
Then you can set about planning all the objects in your apartment you hope to make into future smart surfaces at the earliest possible convenience!