NASA’s Dawn spacecraft went dark last year, but data collected by the craft is continuing to be used to make discoveries about the dwarf planet Ceres that it orbited.
Ceres is an object in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter with a radius of 473 kilometers (294 miles). This makes it too small to be considered a proper planet but far larger than most asteroids, so it is therefore categorized as a dwarf planet, like Pluto. Ceres is the largest object in its asteroid belt which made it a good target for study, and astronomers have long been interested in its dramatic terrain.
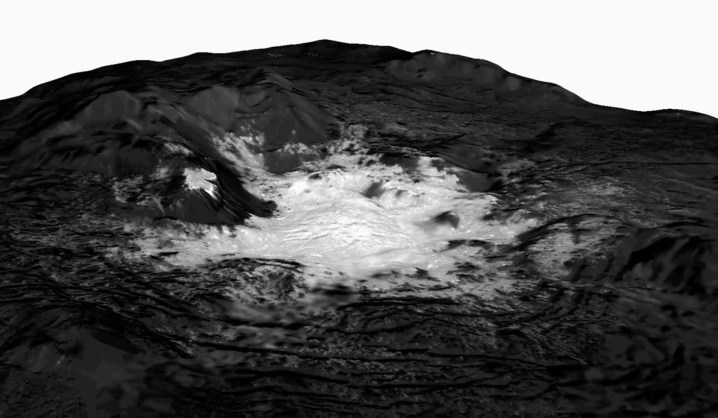
The Dawn mission captured detailed images of the surface of Ceres which show craters and mountains, and even suggest that the planet may still be active. Now a team is studying this data in depth to learn more about one of the stranger findings on the planet: bright white spots at the bottom of impact craters.
These spots are the remnants of cryomagma, salty water from underground reservoirs which is moved up to the surface of the planet in a process similar to the movement of magma in a volcano. These ice volcanoes, called cryovolcanoes, form on bodies with icy shells like Ceres or Europa, one of the moons of Jupiter, and are believed to be important for mixing chemicals to create the kinds of complex molecules which are needed for life.
“Cryovolcanism looks to be a really important system as we look for life,” lead author Marc Hesse, associate professor at the Jackson School of Geosciences, University of Texas at Austin, said in a statement. “So we’re trying to understand these ice shells and how they behave.”
As the white spots were found within craters, this suggests that the cryomagma reservoirs could have been created by powerful asteroid impacts millions of years ago which generated heat and energy to “jumpstart the geology” in the region. When over time fractures formed in the surface, the cryomagma pushed its way up and reached the surface before drying out to leave a deposit of bright white salt on the planet.

The study is published in the journal Geophysical Research Letters.



