Déjà vu, for those who haven’t experienced it before (or have you?), refers to the strange sensation that a certain event or experience you have is one you’ve experienced before. Exactly how it works has long been a source of mystery — with one of the main reasons it’s hard to study being just how unpredictable it is.
“The frustrating thing about déjà vu is that, while it’s something most people have experienced, it’s something which happens relatively infrequently,” Akira O’Connor, a lecturer in the School of Psychology and Neuroscience at the University of St. Andrews in the UK, told Digital Trends. “That means that getting the opportunity to measure it is a very difficult thing. We’ve had to rely on people’s retrospective evaluations of the experience.”
That is changing, however. O’Connor and a fellow researcher are using a method to replicate déjà vu in laboratory conditions that works in the majority of people — using a technique for eliciting false memories. This involves giving people a list of words linked by a common theme, like “night,” “dream” and “pillow” — and then asking them whether they had heard the word “sleep.” When they respond in the affirmative, they are then asked if any of the words they heard started with the word “s” (to which they respond negatively), resulting in a confusing sense of déjà vu.
“Déjà vu is characterized by having a false sensation of familiarity, alongside the awareness that that sense of familiarity cannot possibly be correct,” O’Connor said. “It’s a memory clash where there’s false familiarity, together with an objective awareness that it can’t be real.”
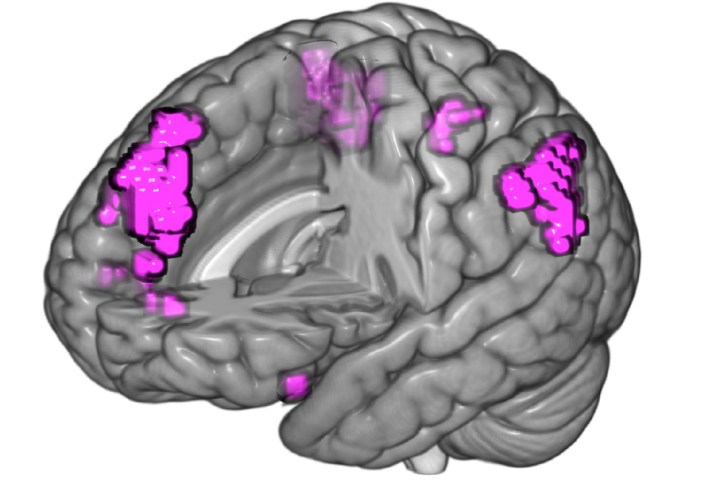
Able to recreate the sense of déjà vu in around two-thirds of participants, O’Connor noted that the “strike rate” was good enough for the project to move onto its next phase: scanning the participants with a functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) machine to see which brain regions lit up when the experience took place.
“What we found was that it wasn’t memory-linked regions that are driving déjà vu,” he said. “Traditionally, researchers thought déjà vu was being driven by false memories. What it actually is is that the cognitive control, error-monitoring conflict-checking frontal brain regions are the ones which show greater activity in people reporting the experience.”
O’Connor told Digital Trends that the work was interesting to him as a memory researcher because it demonstrates that memory decision-making has two distinct phases. “There are the memory signals that are coming through all the time, and also an evaluation of those signals that helps us make sense of all of these various brain inputs — combining them into one coherent stream of useful consciousness,” he said.
While all of this might sound interesting in a “lab science” kind of way, however, it does also have a practical application. Déjà vu has often been associated with neurological disorders. Early researchers attempted to discover a link between déjà vu and mental disorders like anxiety, dissociative identity disorder, and schizophrenia. While these researchers failed to find anything substantive, there are most certainly a variety of health and brain conditions associated with déjà vu. For instance, people who suffer from temporal lobe epilepsy will often experience it as part of their pre-seizure aura: the feeling of impending doom that often occurs before an attack. There are also certain dementia patients who will start to experience déjà vu as their symptoms progress and worsen.
But while it may therefore be tempting to therefore suggest that déjà vu is a negative experience, O’Connor’s work suggests this is not the case. “In some ways our work is reassuring,” he said. “It shows that déjà vu is not a memory error. It’s not a problem associated with your memory; potentially it’s a sign of your overall reasoning and cognition being in rude health. It means you’re able to spot a lot of these errors that are happening and carry on as if they’re not happening.”
O’Connor recently presented his findings at the International Conference on Memory in Budapest, Hungary, after which they were first reported on by New Scientist. He is currently working on a paper to be published.


