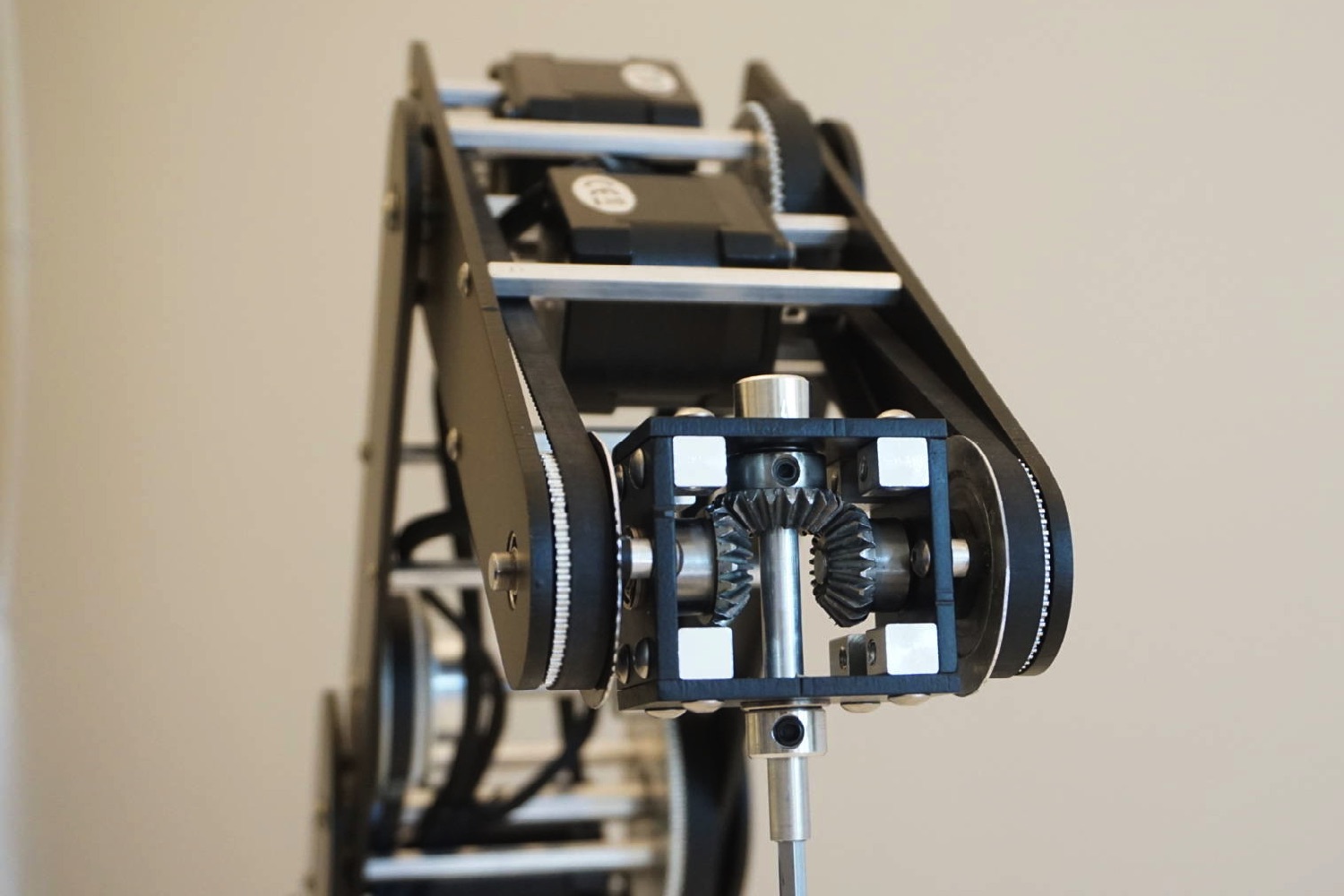
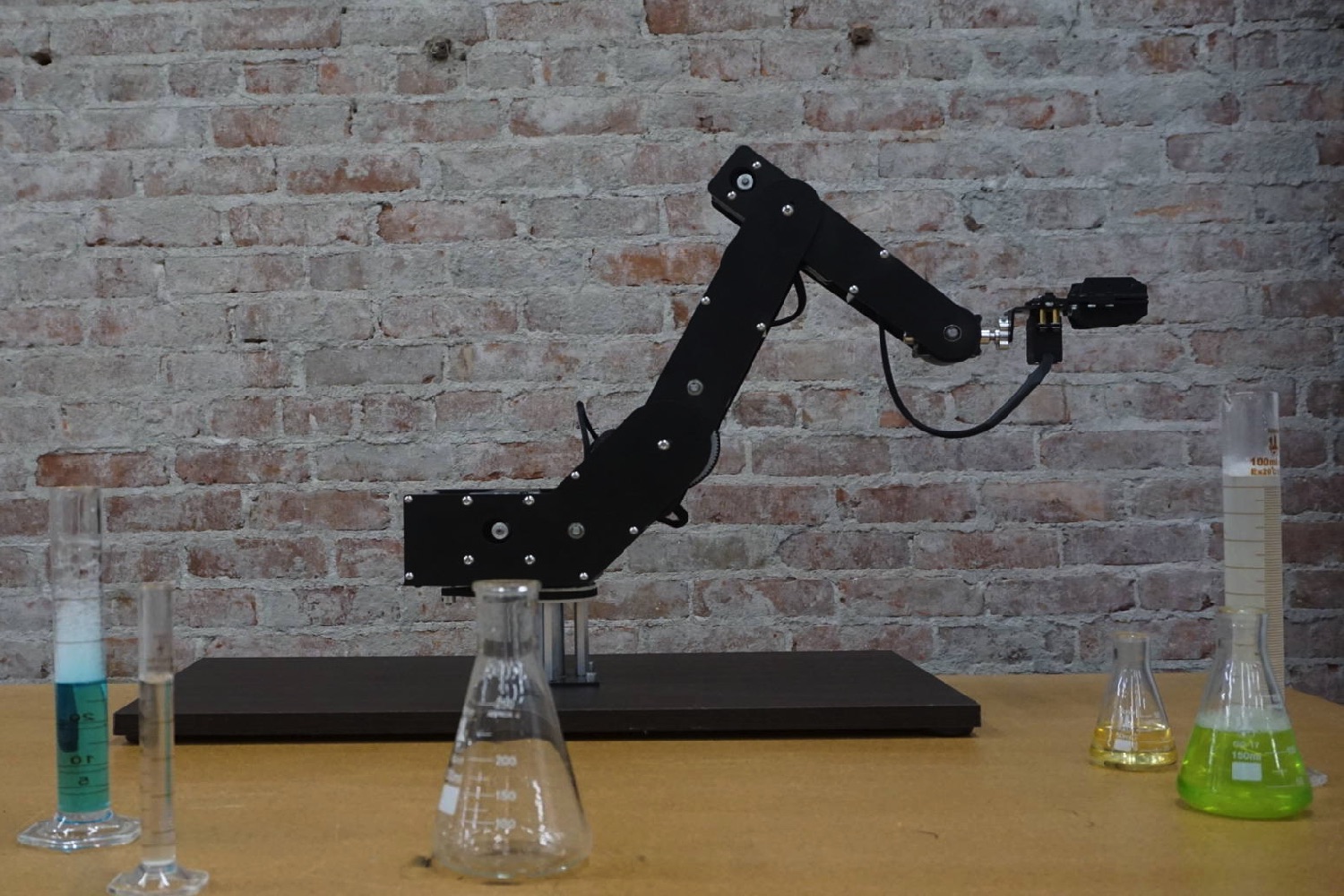
“Compared to other robots in a similar price range, Dorna is sturdier, more powerful, and more accurate,” Sadegh Tabatabaei, one of the creators of Dorna, told Digital Trends. “Dorna can easily handle 2.5 pounds of payload when fully extended, while other competitors can usually handle one pound, at most. Also, Dorna is extremely accurate. You can expect 0.001-inch repeatability, which is significantly better than similar-priced robots, and is comparable to industrial robots priced at more than $50,000.”
While we have not had the chance to put Dorna through its paces, its creators promise that it will deliver a high-quality finish, with a body crafted from aerospace grade aluminum, and precision components used to achieve a sturdy and accurate and powerful robotic arm.
“Our ideal user is anyone who wants to get serious in robotics without spending a fortune on an industrial robotic arm,” Tabatabaei continued. “You can be a student, artist, researcher, or just a home user and find an application for Dorna in your daily tasks. Anyone with basic knowledge of computers, without knowing any specific programming language, can use Dorna. We have created a user-friendly software, called Dorna Lab, that you can use to control it by jogging around the robot to the points that you are interested in, and then asking the software to play the points consecutively and smoothly to complete a task.”
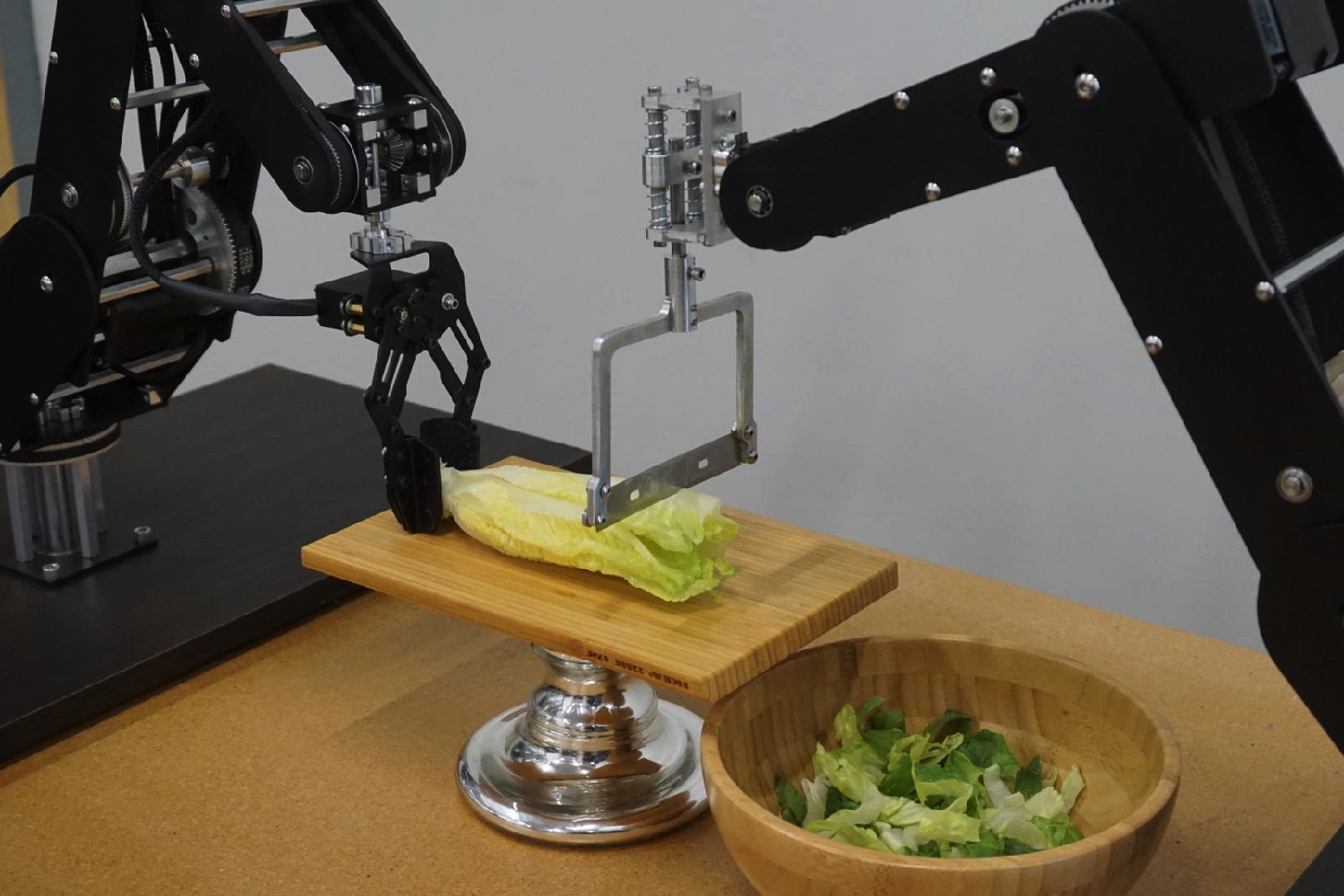
For advanced users, there is also the opportunity to write more complicated scripts, while the fact that the software and APIs are open-source means that hackers and researchers can modify or improve the software based on their own requirements. Along with the robot arm itself, Dorna can come packaged with different tool heads, including camera attachment, servo gripper, 500mw laser engraver, and two-way tool holders.
In all, it is a tantalizing prospect, and — while not the first robot arm we covered at Digital Trends — if it can deliver on its promises, it could certainly have the makings of one of the best. If you would like to get hold of a unit, you can currently pre-order Dorna on Kickstarter, where prices start at $890 for an unassembled kit. Shipping is set to take place in June.