Harvesting water from fog isn’t just a chore for young Luke Skywalker — it’s become an important part of bringing clean water to people living in drought-prone climates across the globe. The problem is that harvesting tools can be pretty inefficient.
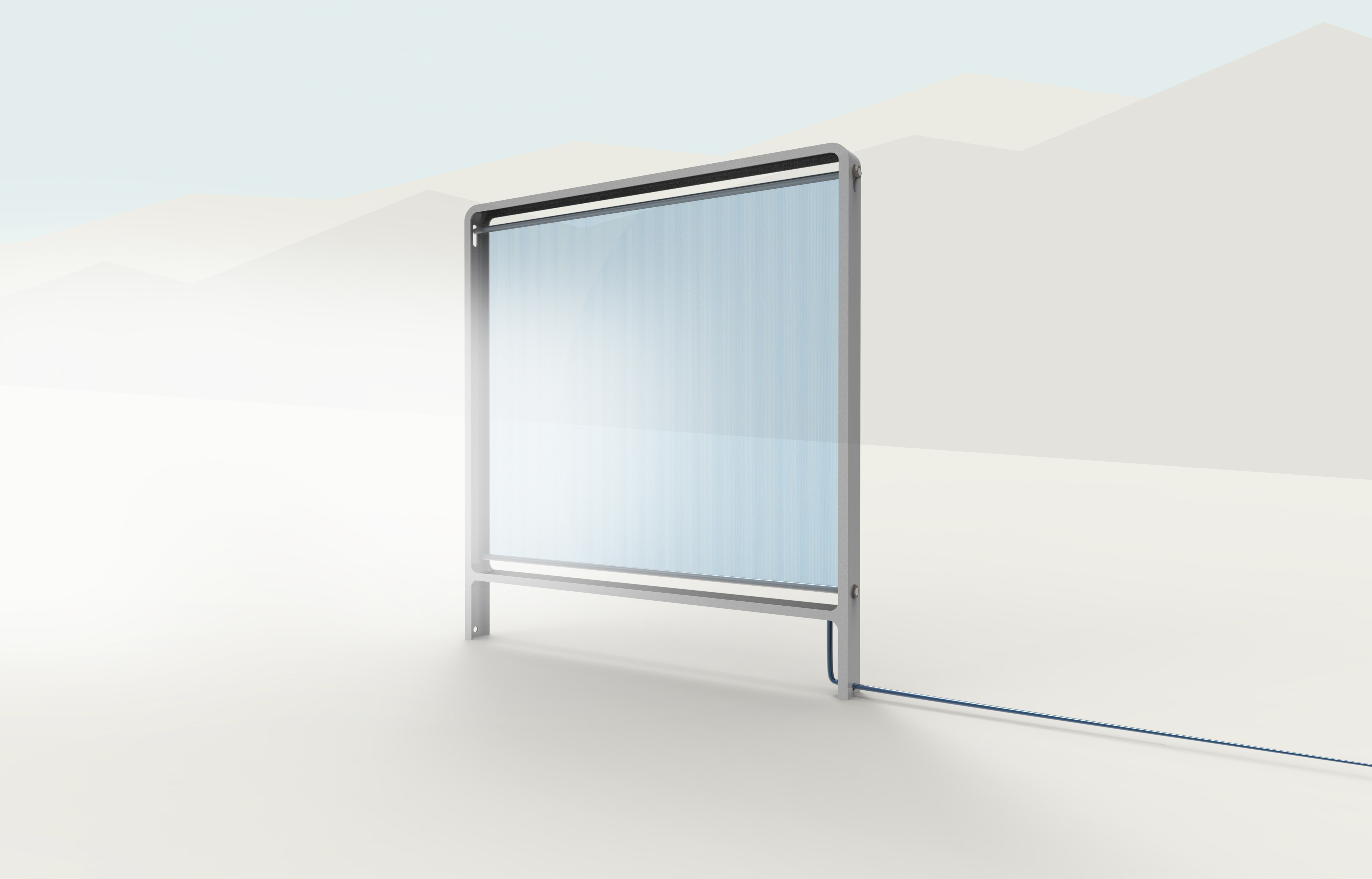
Now, engineers from Virginia Tech have designed a device that may be able to extract three times as much water from fog as previous tools. They’re calling the device the “fog harp” because the secret is in the way its array of parallel wires lines up like the strings of the instrument.
Most fog harvesters used today are massive nets that capture water droplets blown in by the wind. The droplets merge on the net and then stream down to a collection container at the bottom. If the net’s holes are too large, the droplets sneak through. If they’re too small, the holes can get clogged.
“What we demonstrated here is that using a ‘harp’ geometry, rather than nets, can solve the clogging problem to maximize the efficiency of fog harvesters,” Jonathan Boreyko, a Virginia Tech engineer who worked on the project, told Digital Trends. “By only having vertical, parallel wires, the droplets are able to slide down into the collector at very small sizes, preventing clogging even when small wires are used. So our harps can both catch the fog efficiently from the air, and avoid the clogging problem that plagues conventional nets.”
Some four billion people face severe water scarcity, according to a report from 2016, and their situation may worsen if the effects of climate change intensify. Since the 1980s, fog nets have helped drought-prone communities with access to low, moving fog, with the largest fog nets able to collect some 6,000 liters of water each day.
In the lab, the fog harp was able to increase water capture threefold compared to traditional devices. The current fog harp prototype is three feet by three feet, but the Virginia Tech team aims to increase the size in future iterations. By overcoming the constraints of traditional fog nets, the team hopes the fog harp will offer a tool that effectively captures droplets and avoids clogging.
“Fog harvesting is already used to obtain fresh water in arid regions, particularly along the coastal regions of South America and Africa,” Boreyko said. “When rainfall is scarce, fog becomes an invaluable source of water for drinking and agricultural purposes. Many desert animals and plants know this too, for example the pointy needles of cacti are highly efficient at capturing fog from the air.”
A paper describing the project was published this week in the journal ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces.


