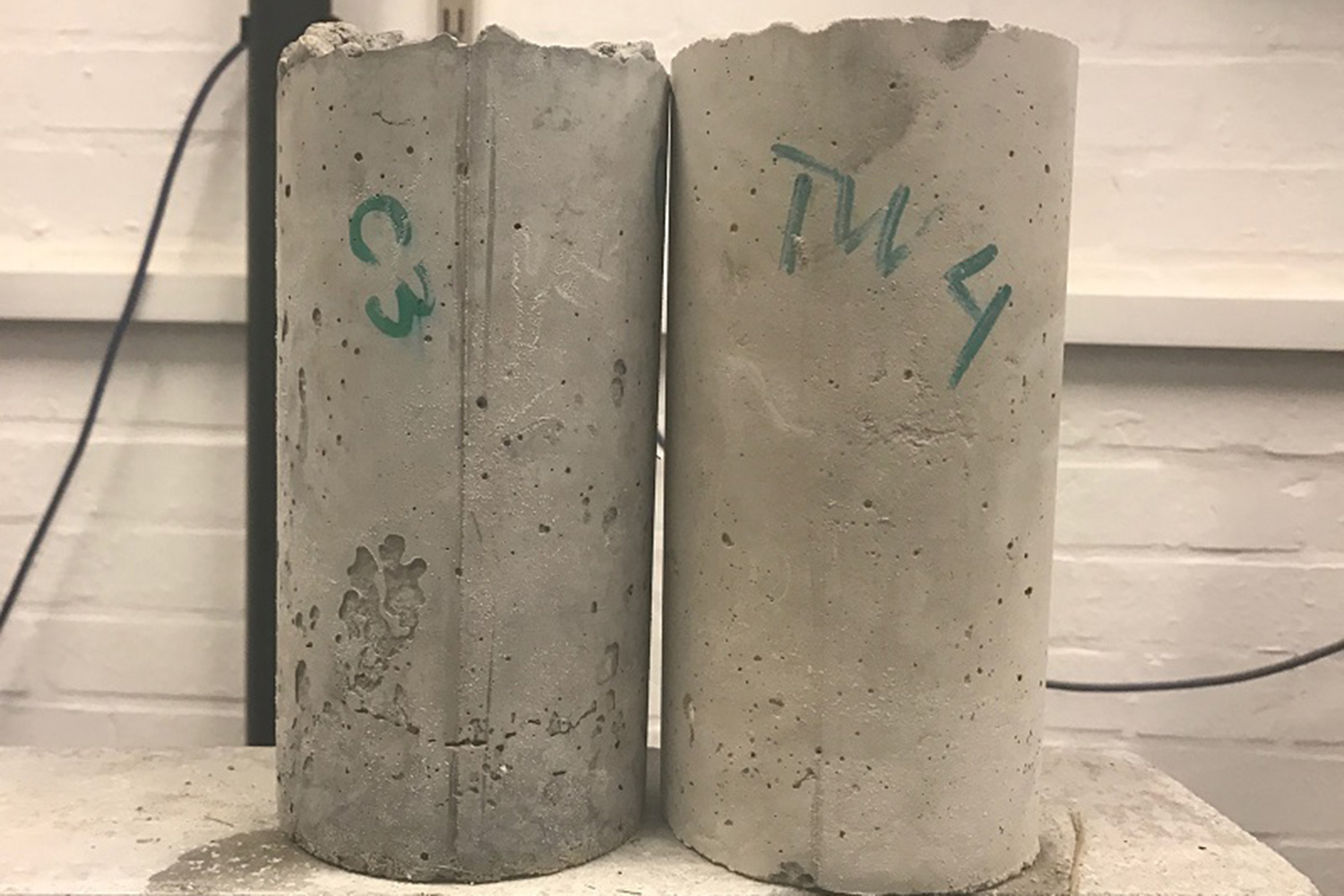
Concrete isn’t the sexiest building material, made up of little more than cement, water, and rocks. It’s neither as strong as steel nor as flexible as wood, but without it our world would look a lot different. From sidewalks to skyscrapers, concrete plays a major role in construction, both inside and out.
Now, researchers from the University of Exeter have created a new concrete production technique that reinforces the material with graphene. In a study published this week in the journal Advanced Function Materials, the researchers describe how the composite material — which they’ve taken to calling GraphCrete — is at least two times as strong and four times more water-resistant than conventional concrete, and could make future construction more sustainable and environmentally friendly.
“Nearly 10 percent of global carbon emissions are due to cement and concrete use,” Monica Craciun, professor of nanoscience at University of Exeter and co-author of the study, told Digital Trends. “We demonstrate a new perspective for reinforcing traditional concrete on the nanoscale level, which has great impact on its mechanical properties.”
To do so, Craciun and her colleagues used graphene, the semi-metal that is often called a wonder material for its seemingly endless applications. In the recent research, a graphene concentrate was used to fortify concrete in its early formation, doubling its compressive strength and making it almost four times more water-resistant.
“What does this mean?” Craciun said. “You can use twice as less concrete per cubic-meter and still achieve the same strength. Or, alternatively, in areas of the world subject to flooding you can increase the life and durability of any building. In short, our graphene reinforced concrete can contribute to significant decrease in carbon emissions due to improved strength and durability.”
The increased strength and durability would also make GraphCrete desirable for developers who want to build bigger buildings.
Graphene is notorious for rarely making it out of the lab. However, Craciun is confident she and her team will find real-world applications for the research soon.
“We are currently exploring the business case for Graphene Nano Additives that can enhance the physical properties of composite materials,” she said, adding that they are looking for stakeholders interested in exploring business cases for their technologies.


