The company launched a new VR-tracking system on Thursday that is expected to create a boom in the theme park-scaled VR arena market throughout 2017 and 2018. It’s called OptiTrack Active and throws out the reflectors used in older systems to track objects and users. Instead, the new system relies on embedded infrared LEDs and small, high-resolution cameras/trackers that can be mounted essentially anywhere.
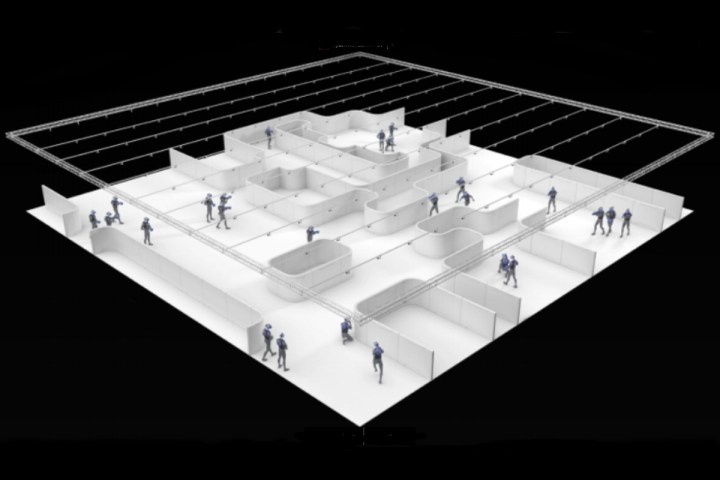
To better understand what is going on, let us back up for a second. Arena-sized VR experiences require the user to wear an HMD that is tethered to a backpack-style PC. A typical shooter scenario would have the user wear the HMD, the backpack PC, fake body armor, and a fake weapon. These items would include reflectors arranged in unique configurations so that the cameras and tracking system can keep up with each individual object.
But that setup can be a problem when VR experiences require large stationary objects and multiple rooms. According to OptiTrack, this “passive” system is great for research VR and experiences with lots of open space.
However, with OptiTrack Active’s infrared LEDs, the system can track people and objects based on pulses not seen by the human eye. The system relies on one matchbox-sized printed circuit board installed on each device to be tracked, which controls up to eight LEDs. The system also includes a base station installed at the center of the VR experience that keeps the LEDs synced with OptiTrack’s new low-latency Slim 13E cameras, or the Prime 13W cameras.
One of the benefits of using the new tracking system is that developers can design a single HMD, weapon, or other object that can be manufactured over and over. By contrast, with the previous passive system, each object design could generally look the same overall, but each one was essentially a single manufactured design due to their unique (and costly) reflector configurations.
“We heard the market loud and clear — the leaders in the out-of-home VR space wanted all the tracking performance that OptiTrack systems deliver, but with a way that allows them to build and deploy 500 identical HMDs, not 500 slightly different configurations. The result is the best active tracking system ever built and the lowest cost to rollout to dozens of sites” said Brian Nilles, OptiTrack’s Chief Strategy Officer.
OptiTrack will showcase its Active VR tracking system during GDC 2017. Hopefully, the launch will mean thrill seekers will see more theme park-style VR arenas pop up across the nation over the course of 2017.


