There are reasons why wave energy is one of nature’s greatest untapped resources. The ocean is unforgiving. Salt water corrodes small parts on metal machinery. Waves can be a brutal and unpredictable force. But that same force makes the ocean an eternal source of kinetic energy, ripe for the harvest if only we can conquer it. In fact, the United States could power one-third of its electricity if engineers could develop a means to harness the wave energy along its coasts.
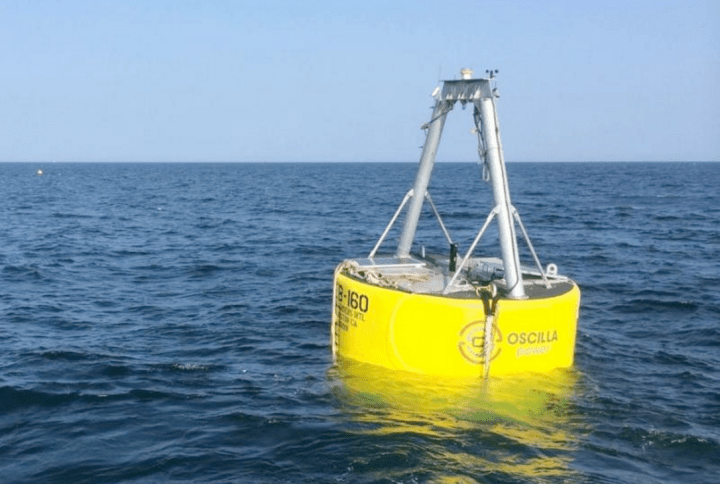
A team of researchers and engineers at Oscilla Power have taken on that challenge with hopes to succeed where so many others have failed. With a unit called Triton Wave Energy Converter (WEC), Oscilla has re-envisioned how power can be generated from wave energy.

Triton is a two-bodied wave energy device comprised of a surface float up top and a ring suspended in the ocean below. From above the device looks like a barge. From below, Triton looks like some kind of mechanical jellyfish. As the surface float undulates with the waves, the suspended ring resists that motion. This resistance generates energy.
Previous machines designed to convert waves into usable energy have proven to be too fragile, complex, and expensive for the unforgiving force of the ocean. Small parts corrode when exposed to salt water for too long, and the oceans unpredictability means it’s often economically unviable to install and maintain machinery.
Oscilla thinks moving parts have doomed previous designs, so the company sought to remove these from their device. Where most other electric generators use displacement or the rotation of a turbine to generate energy, the Triton squeezes metal alloys to create alternating magnetic poles in the metal.
Triton may be billed as a simplified energy conversion system, but it isn’t a small one. The full-scale device measure almost 100 feet in length. At this size, Oscilla says each Triton will be able to deliver more than 600kW on average – an intriguing promise, but definitely one we’ll want to see before we believe.


