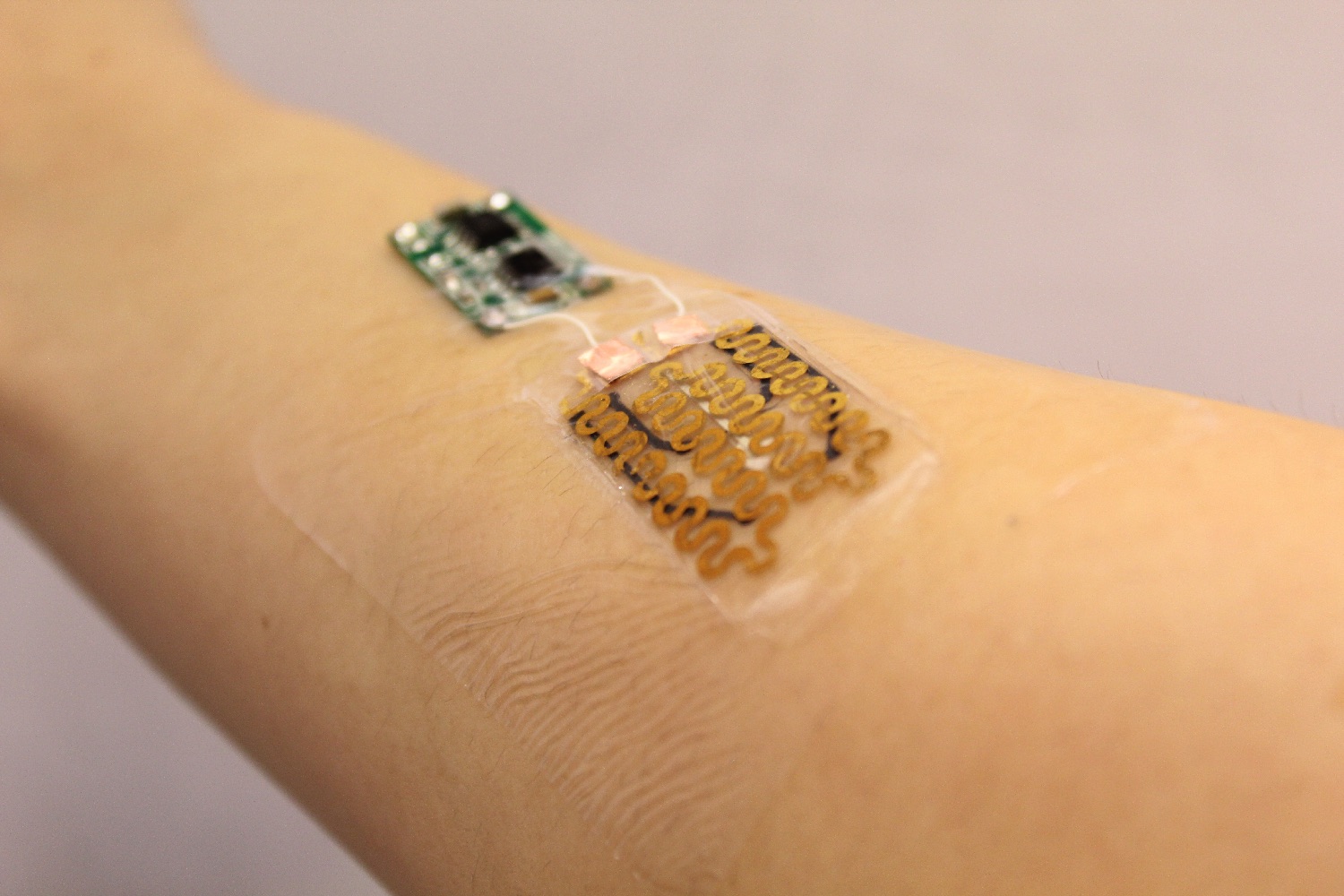
Here at Digital Trends we have covered a surprising number of fascinating high-tech wound dressings, such as one made of spider silk and a futuristic Star Trek-style patch, which uses cold plasma as part of the healing process. Adding to this growing subgenre of stories is a new smart bandage developed by researchers at the University of Nebraska-Lincoln. Not only is it capable of checking whether a wound is infected, but it can also proactively treat it with medication if it deems this to be the case.
“We have developed an automated and smart bandage that can measure the level of pH, and use that for identifying potential infection in chronic wounds and deliver antibiotics if infection is detected,” Ali Tamayol, an assistant professor in the department of mechanical & materials engineering, told Digital Trends. “This platform reduces the number of hospital visits by patients, and facilitates quick treatment of infection in wounds to reduce the life threatening complications associated with that.”
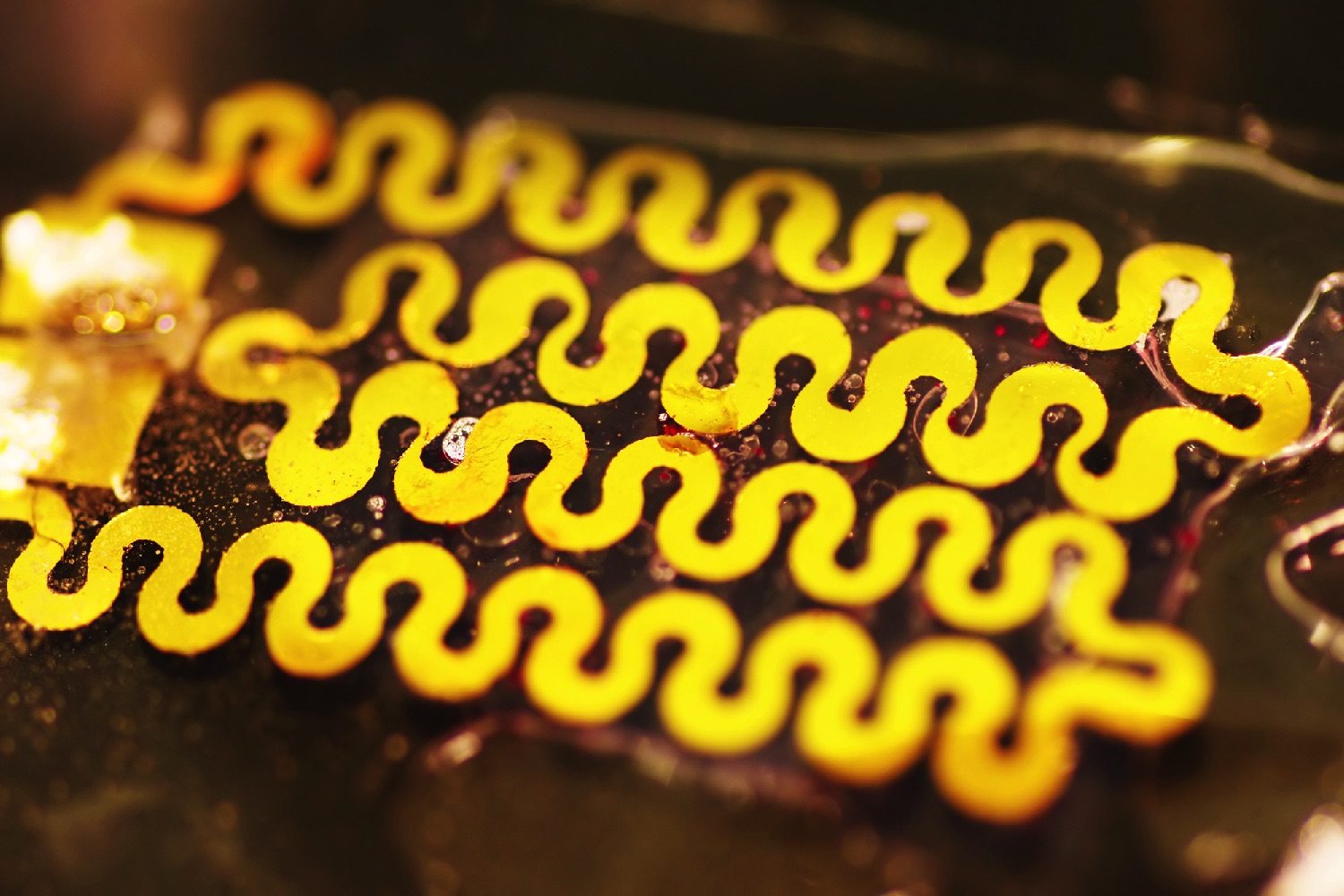
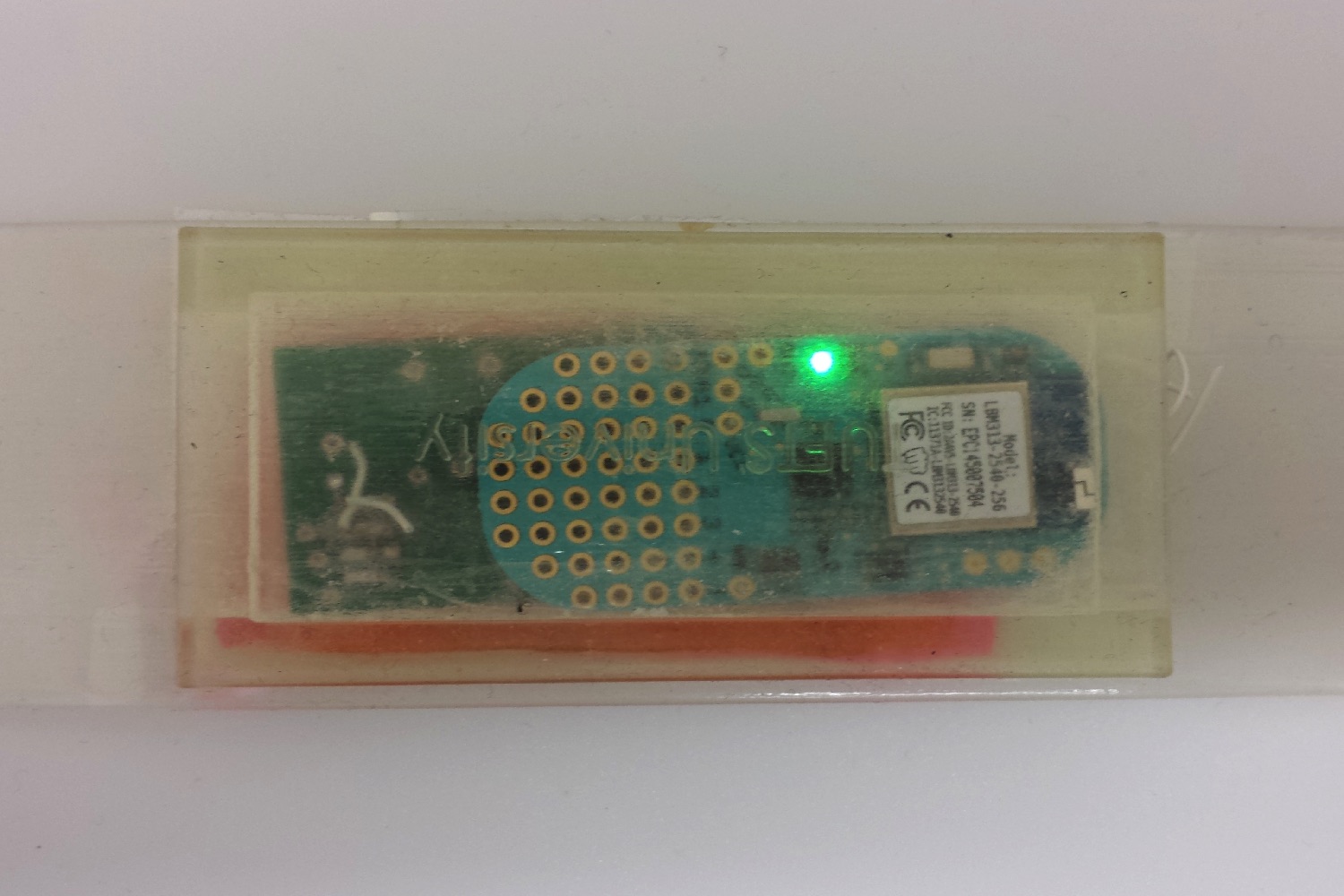
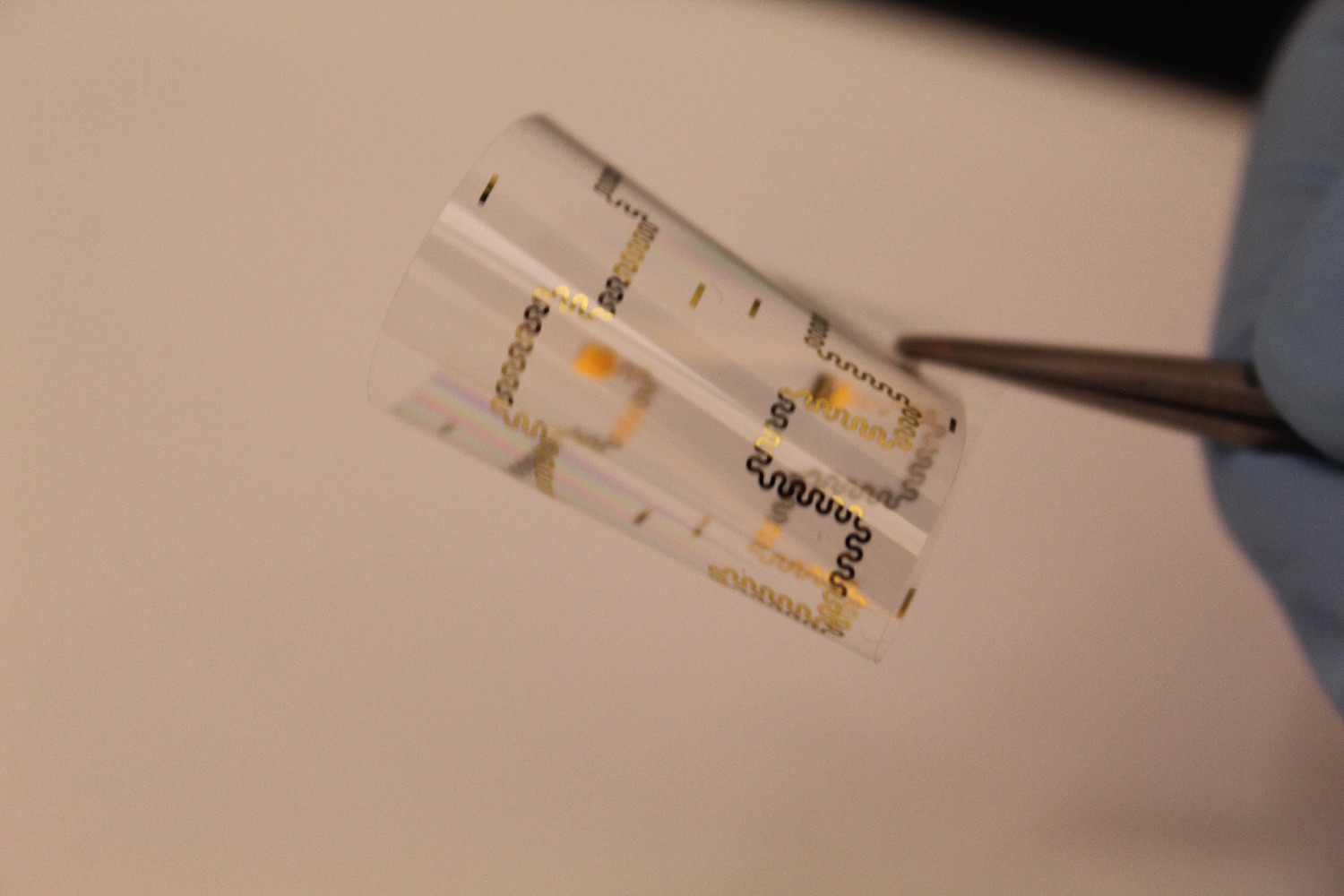
The smart wound dressing contains both pH and temperature sensors. Between them, these two sensors can tell when a wound turns more alkaline, thereby signalling the presence of bacteria, as well as the presence of inflamation. The sensors are located in a hydrogel sheet, which carries capsules containing medicine, including antibiotics. If an infection is detected, the bandage can automatically release the drugs. In tests, it was able to wipe out more than 90 percent of bacteria, and bring pH levels back within normal range.
“The treatment of chronic diabetic wounds is an immediate application,” Tamayol explained. “However, this approach can be extended to other chronic diseases in which drugs should be delivered to control the level of biomarkers. For example, a similar platform can be used for controlling the level of glucose in patients suffering from diabetes.”
The next stage in the development process will involve improving the drug delivery platform, along with testing the bandage on small animal models. Should this be a success, hopefully it won’t be long before clinical trials on humans might be carried out, prior to this becoming a standardized tool available to physicians. “There are many people suffering from chronic wounds, and my hope is to find a solution to help them out,” Tamayol said.
A paper describing the work was recently published in the journal Small.