
At Mobile World Congress 2024, Qualcomm is adding more to its portfolio of AI-on-phone tricks facilitated by the Snapdragon series silicon for Android phones. The chipmaker has already showcased some impressive AI capabilities for the Snapdragon 8 Gen 3 flagship, such as voice-activated media editing, on-device image generation using Stable Diffusion, and a smarter virtual assistant built atop large language models from the likes of Meta.
Today, the company is adding more grunt to those AI superpowers. The first is the ability to run a Large Language and Vision Assistant (LLaVa) on a smartphone. Think of it as a chatbot like ChatGPT that has been granted Google Lens abilities. As such, Qualcomm’s solution can not only accept text input, but also process images.
For example, you can push an image depicting a charcuterie board and ask questions based on it. The AI assistant, based on a large multimodal model (LMM) that can process over 7 billion parameters, will then tell you all the kinds of fruits, cheeses, meats, and nuts on the board depicted in the input image seen below.
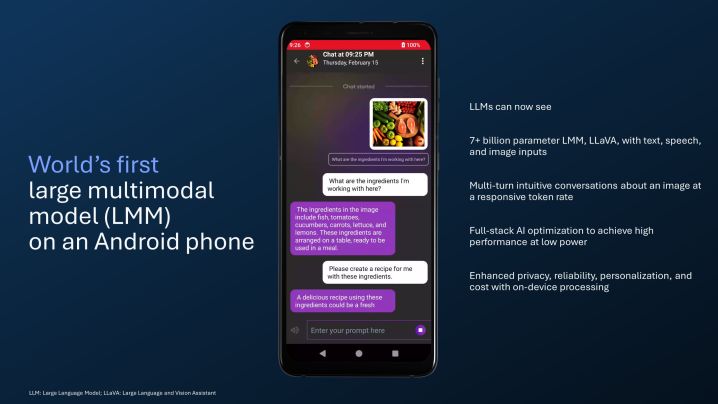
It can also handle follow-on queries, so you can conduct a flowing back-and-forth conversation. Now, the likes of ChatGPT have also gained multiple-modal capabilities, which means OpenAI’s tool can also process image inputs. However, there’s a crucial difference.
Products like ChatGPT and Copilot are still very much tethered to a cloud-based architecture, meaning your data is handled on remote servers. Qualcomm’s push is in the direction of on-device processing. Everything happens on your phone, which means the whole process is faster, and there is little risk of privacy intrusion.
“This LMM runs at a responsive token rate on device, which results in enhanced privacy, reliability, personalization, and costs,” says Qualcomm. Whether Qualcomm’s promised LLaVa-based virtual assistant will arrive as a standalone app or if it will carry a fee is yet to be officially confirmed.
The next announcement from Qualcomm dives into the creative domain of image generation and manipulation. Not too long ago, Qualcomm demoed the world’s fastest text-to-image generation on a phone using Stable Diffusion tech. Today, the company is giving a first glimpse of LoRA-driven image generation.
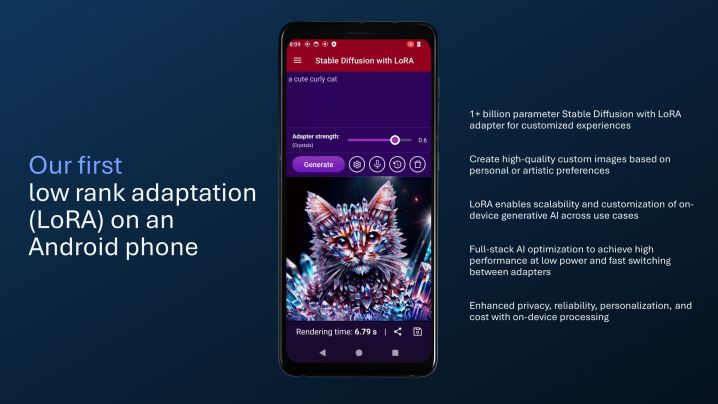
LoRA takes a different approach to image generation than a regular generative AI tool such as Dall.E. LoRA, short for Low-Rank Adaptation, is a technique developed by Microsoft. Training an AI model can be quite cost-prohibitive, high on latency, and particularly demanding from a hardware perspective.
What LoRA does is it dramatically reduces the model weight, a goal that is achieved by only focusing on specific segments of the model and reducing the number of parameters for training purposes. In doing so, the memory requirements go down, the process becomes faster, and the amount of time and effort it takes to adapt a text-to-image model also drops dramatically.
Over time, the LoRA distillation technique has been applied to the Stable Diffusion model for generating images from text prompts. Owing to the gains in efficiency and the easier adaptability of LoRA-based models, it is seen as a tailor-made route for smartphones. Qualcomm certainly thinks so, and even rival MediaTek has embraced the same solution for generative AI tricks on its flagship Dimensity 9300 chip.
Qualcomm is also showcasing a few other AI tricks at MWC 2024, some of which have already appeared on the Samsung Galaxy S24 Ultra. Among them is the ability to expand the canvas of an image using generative AI fill and AI-powered video generation. The latter is quite ambitious, especially after seeing what OpenAI has accomplished with Sora. It would be interesting to see how Qualcomm manages to port it over to smartphones.




