
Chemists at UC Riverside have developed material that can repair itself from cuts and scratches. They’ve torn it in half and observed it stitching itself back together in less than 24 hours, and they’ve stretched it to 50 times its original size, only to see it remain functional.
The secret is a forgiving chemical bond between molecules.

Two bonds exist in materials, Chao Wang, a chemist leading the self-healing materials research, explained to Science Daily: Covalent bonds, which are strong and don’t readily reform once broken; and non-covalent bonds, which are weaker. The hydrogen bonds that connect water fit into the former, non-covalent category — they break and reform constantly, giving water its fluid property.
The polymer that Wang’s team developed is held together by an ion-dipole bond, a force between charged ions and polar molecules. A polar, stretchable polymer and an ionic salt link tightly together — enough to pull the material together when it breaks.
This material is especially well suited to smartphones because it conducts electricity, Wang told Business Insider. Capacitive touchscreens have electrodes underneath that complete a circuit when in contact with conductive material. That’s how phones recognizes taps, touches, and swipes.
Self-healing smartphone materials aren’t new — the back cover of LG’s G Flex can heal itself from small scratches. But they couldn’t conduct electricity.
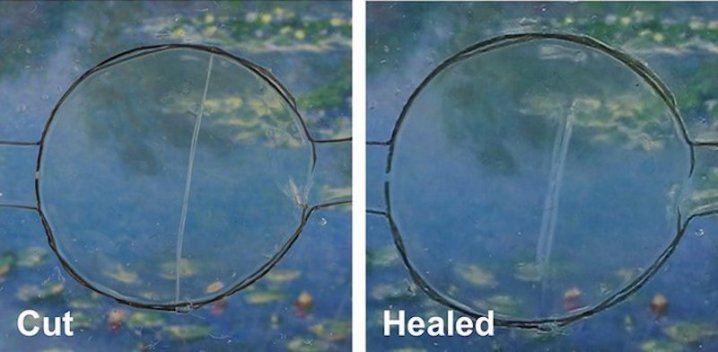
Going forward, the researchers hope to improve the material’s properties. They’re testing it in harsh conditions, such as high humidity. “Previous self-healing polymers haven’t worked well in high humidity,” Wang told Science Daily. “Water gets in there and messes things up. It can change the mechanical properties. We are currently tweaking the covalent bonds within the polymer itself to get these materials ready for real-world applications.”
Wang predicts that this new self-healing material will make its way into phone screens and batteries by 2020.
“Self-healing materials may seem far away for real application, but I believe they will come out very soon with cellphones,” he told Business Insider. “Within three years, more self-healing products will go to market and change our everyday life. It will make our cellphones achieve much better performance than what they can achieve right now.”


