People have long complained of painful “tech neck” from overusing their smartphones, but now there’s evidence to suggest young people might be growing actual horns because of phone use.
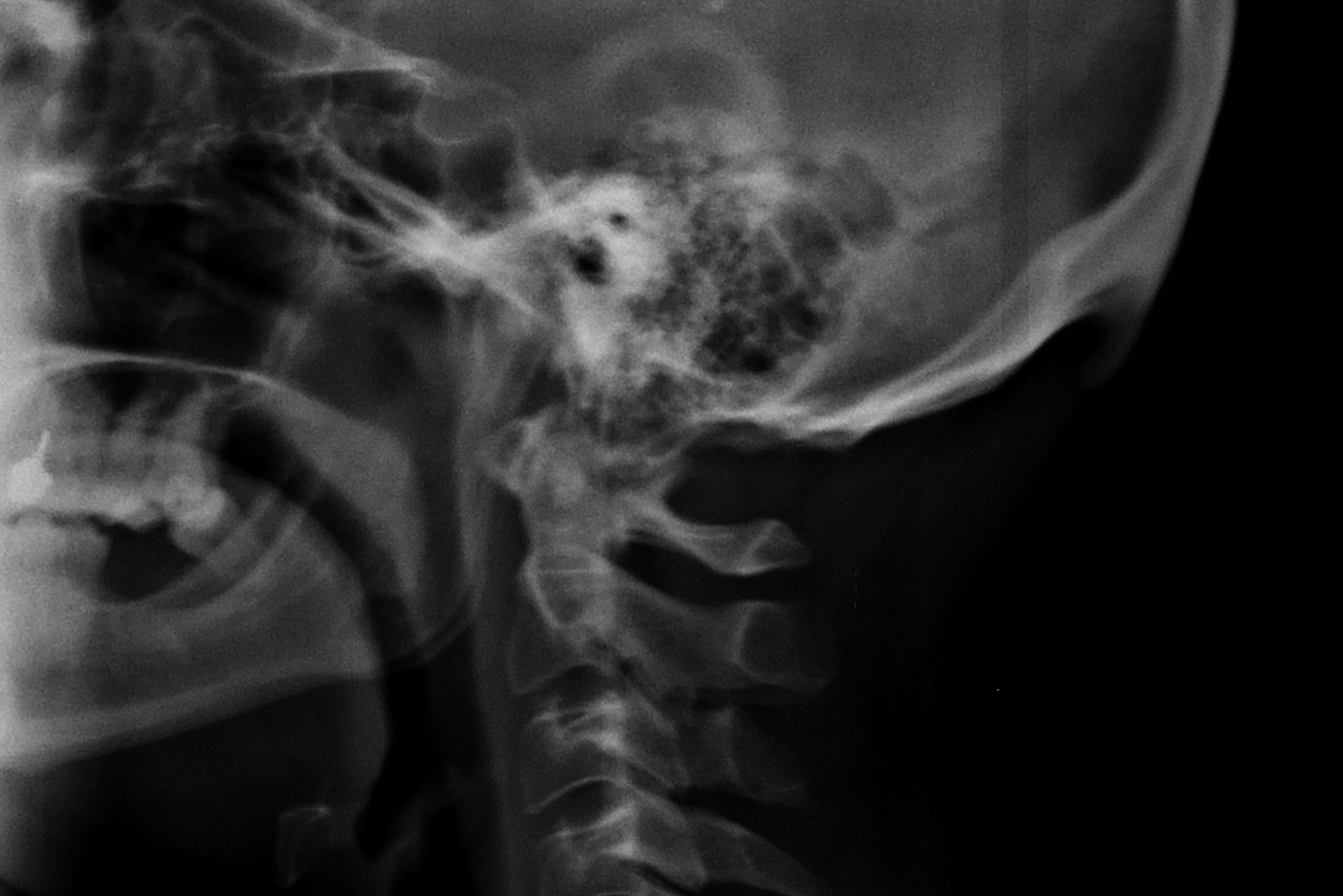
Researchers from the University of the Sunshine Coast in Queensland, Australia have recently found bone growth at the base of young adults’ necks, which looks like a horn jutting out from the skull, the Washington Post reports. The researchers attribute this new growth to consistent bending of the head when using smartphones or handheld devices.
The research paper looked at 218 X-rays of young adults ages 18 to 30 and found that 41% had bone growth. Men had the specific bone growth more than women, according to the study. The size of the bone growths suggest that they took a long time to develop, most likely from childhood, so while smartphone use may not be completely linked to the growth, researchers say it could be likely.
It’s already known that smartphone and computer use can cause carpal tunnel or tendonitis. And tech neck causes the neck to reverse its curve from a backward curve to a forward curve, creating not only strain on your neck but your spine as well. Even our eyes are working harder from all the blue light we take in from our devices.
While these types of problems show up from the overuse of devices, finding actual horns growing out of our necks is the among the first instances of technology literally be changing the evolution of our bodies.
We could definitely be smarter when it comes to using our smart devices. Taking frequent breaks throughout the day to give your eyes, neck and hands a break could prove useful. There’s also a lot of talk lately about digital detoxes, which entails refraining from any use of technology for a certain period of time for both physical and mental health benefits.
You don’t have to log off of your devices completely, but check in with your body from time to time before you adapt too much to the tech neck.
“The answer is not necessarily swearing off technology. At least, there are less drastic interventions,” Mark Sayers, an associate professor of biomechanics at Sunshine Coast, told the Washington Post. “What we need are coping mechanisms that reflect how important technology has become in our lives.”



