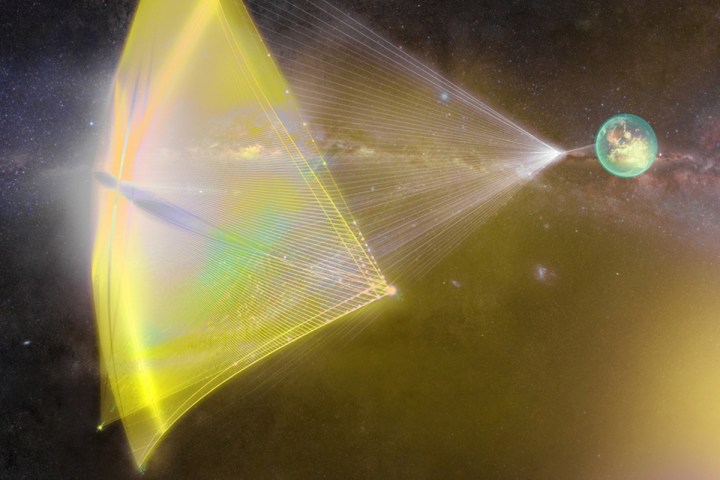
Dubbed Breakthrough Starshot, the project would see a single mothership orbit Earth carrying hundreds of tiny nanocraft called StarChips. Day-after-day, the mothership would deploy a StarChip, which would head toward our nearest neighboring star system, Alpha Centauri, to measure and photograph the system. Powered by a ground-based laser and a massive solar sail, the craft would have a top speed of 20 percent the speed of light, allowing it to make the trip in just 20 years.
The mission is ambitious and, although it’s backed by some of the smartest minds on the planet, a recent study found that it faces some major dangers in outer space.
A team of Harvard researchers associated with the project have been investigating what kind of damage the probes would have to endure on the 25 trillion-mile journey to Alpha Centauri.
The researchers discovered that StarChips face two dangers from heavy atoms and gas floating around in space. For one, collisions with the atoms would wear away at the probe and lead to melting of up to 30 percent of the its mass. Although unlikely, larger particles of space dust could destroy the probe completely.
But the researchers may have a solution. By covering the probes with an additional layer of graphite or beryllium as a buffer, they think they may be able to save StarChips from much of the damage. Meanwhile, the solar sail can either be permanently concealed behind this buffer or folded and retracted as needed.