A new image from the James Webb Space Telescope shows the majesty of the gorgeous Orion nebula in tremendous detail. The European Space Agency (ESA) has shared an extremely high-resolution version of the image that you can zoom into to see the details of this stunning cloud of dust and gas which hosts sites of star formation where new stars are being born.
The full image is available to view in the ESASky application, where you can zoom in a compare images of the same target taken in different wavelengths. There’s also a very large version of the image if you want to download and pursue it at your leisure.
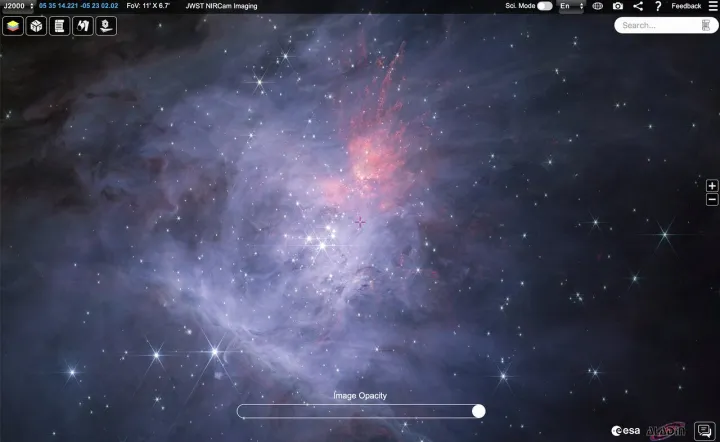
Also known as Messier 42, the Orion nebula is located just to the south of the Orion’s belt constellation and is one of the brightest nebulae in the sky, making it a key target for scientists studying star formation. As new stars are born, those which are young and very hot give off ultraviolet radiation which illuminates the clouds of dust and gas around them. At the heart of this nebula is a group of stars called the Trapezium Cluster, which are young and bright, some of which are up to 30 times the mass of our sun.
This image reveals some cosmic oddities as well. Scientists told the New York Times that the observations included 150 free-floating objects, some of which are in pairs. They are similar to rogue planets that don’t orbit a star, but it’s not clear how they formed within the nebula. “There’s something wrong with either our understanding of planet formation, star formation — or both,” ESA scientist Samuel Pearson told the Times, puzzling over the presence of these objects. “They shouldn’t exist.”
The unusual objects have been named Jupiter Mass Binary Objects, or JuMBOs, and can be smaller than Jupiter but reach temperatures of over 1,000 degrees Fahrenheit. The unexpected discovery suggests there may be aspects of planetary formation that we don’t yet understand.



