Late last month, the Juno spacecraft performed a close flyby of Jupiter’s moon Europa, coming within around 219 miles of the moon’s surface — a mere hair away in spacecraft terms. As the spacecraft whipped by Europa at a relative speed of almost 15 miles per second, it collected data including images from this most intriguing location. And now NASA has released the highest-resolution image Juno has ever taken of Europa, showing its surface in stunning detail.
Europa is a particularly intriguing place due to its potential habitability. Its surface is covered in a thick crust of ice 10 miles deep, but beneath this ice there is thought to be a salt water ocean. That liquid water makes it a potentially habitable environment, so there is great interest in examining the moon in more depth to see if it could possibly host life.
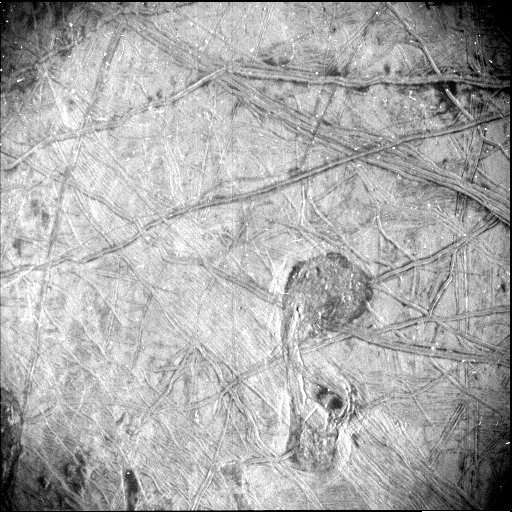
The image of Europa’s surface shows the grooves and ridges in the ice, covering an area of around 93 miles by 125 miles. It was taken by Juno’s Stellar Reference Unit instrument (SRU) which takes black and white images to help the spacecraft point in the right direction by imaging the stars. But researchers have found clever ways to make use of the camera for scientific work as well, particularly in low-light conditions. It was able to snap this image of Europa while the moon was illuminated by light reflected from Jupiter.
“This image is unlocking an incredible level of detail in a region not previously imaged at such resolution and under such revealing illumination conditions,” said Heidi Becker, the lead co-investigator for the SRU, in a statement. “The team’s use of a star-tracker camera for science is a great example of Juno’s groundbreaking capabilities. These features are so intriguing. Understanding how they formed – and how they connect to Europa’s history – informs us about internal and external processes shaping the icy crust.”
Juno was launched in 2011 and was originally intended to only study the planet Jupiter. But in 2021 the mission was extended to include the study of several of Jupiter’s moons: Ganymede, Europa, and Io. It performed a flyby of Ganymede in 2021, has now visited Europa in 2022, and in 2023 it will pass by Io. And the moons of Jupiter are set to be busy in the next decade, as they will also be hosting the NASA Europa Clipper mission and the European Space Agency JUICE (JUpiter ICy moons Explorer) mission.



