NASA’s Juno mission is best known for the gorgeous images of Jupiter that it has taken since its launch in 2011 and arrival at Jupiter in 2016. But the spacecraft hasn’t only investigated the planet — it has also studied Jupiter’s many moons, like the large Ganymede and the icy Europa. Recently, the spacecraft has been making close flybys of the Jovian moon Io, which is the most volcanically active body in the solar system. And it has observed some dramatic features there, like a lake of lava and a large mountain.
Even though Jupiter (and Io) are both far from the sun, and therefore receive little heat from sunlight, Io still has high internal temperatures. That’s because Jupiter is so large that its gravitational pull acts on Io and creates friction, heating it up in a process called tidal heating. Though the surface of the moon is cold, at below minus 200 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 130 degrees Celsius), the volcanoes spewing out material from the planet’s hot interior can reach temperatures of thousands of degrees Fahrenheit.
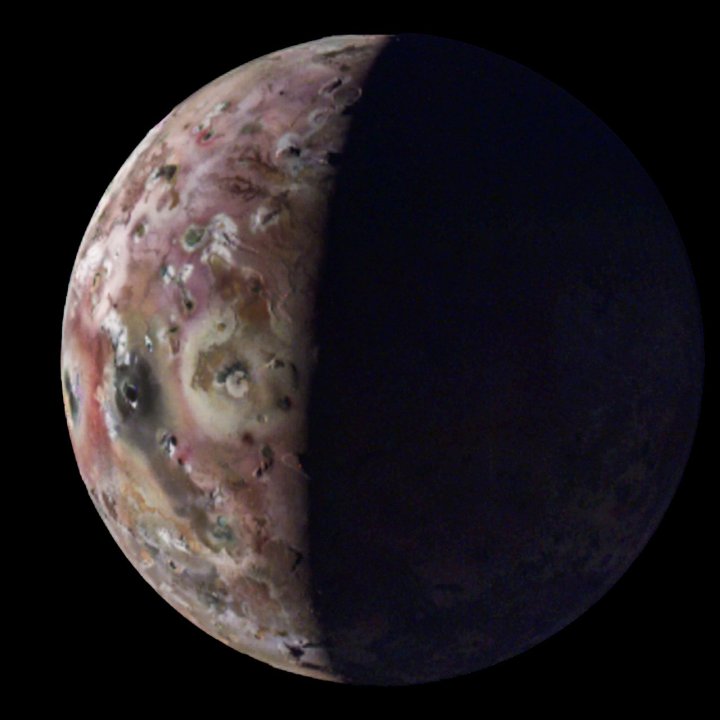
The effects of that heating were seen in action by Juno when it made its recent close passes of Io. “Io is simply littered with volcanoes, and we caught a few of them in action,” said Juno’s principal investigator, Scott Bolton, at a news conference.
“We also got some great close-ups and other data on a 200-kilometer-long (127-mile-long) lava lake called Loki Patera. There is amazing detail showing these crazy islands embedded in the middle of a potentially magma lake rimmed with hot lava. The specular reflection our instruments recorded of the lake suggests parts of Io’s surface are as smooth as glass, reminiscent of volcanically created obsidian glass on Earth.”
The incredible observations have been used to create this artist’s concept video (below) showing what it would look like to fly over this lava lake.
Another striking concept video (below) shows a structure called Steeple Mountain, which spikes dramatically from the surface and is between 3 and 4.3 miles (5 and 7 kilometers) high. The animation shows one side of the mountain in detail while the other side remains in shadow, as Juno only observed one side of the mountain illuminated during its flybys.
Much of this data was collected during Juno’s most recent flyby of Io on April 9, when it came within 3 and 4.3 miles (5 and 7 kilometers). Its trajectory will continue to take it on flybys of Jupiter as well, so researchers hope to learn more about Jupiter, such as details about how the planet formed.



