The groundbreaking James Webb Space Telescope is peering farther into deep space than any observatory that has gone before, but it’s also producing breathtaking images of celestial bodies closer to home.
Take this awesome shot of Jupiter, for example.
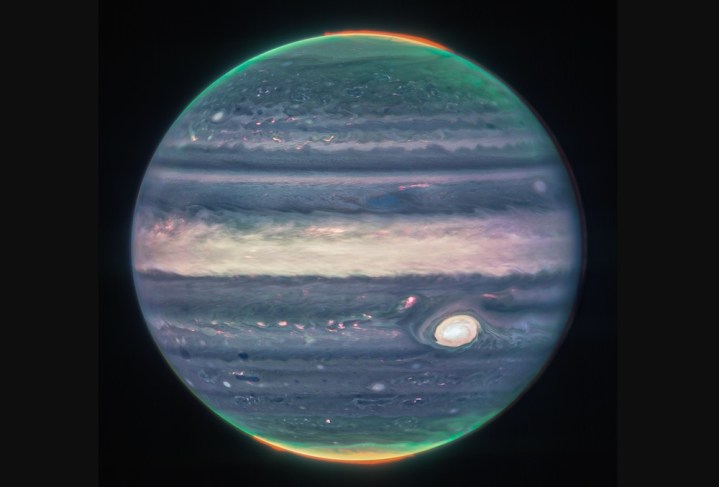

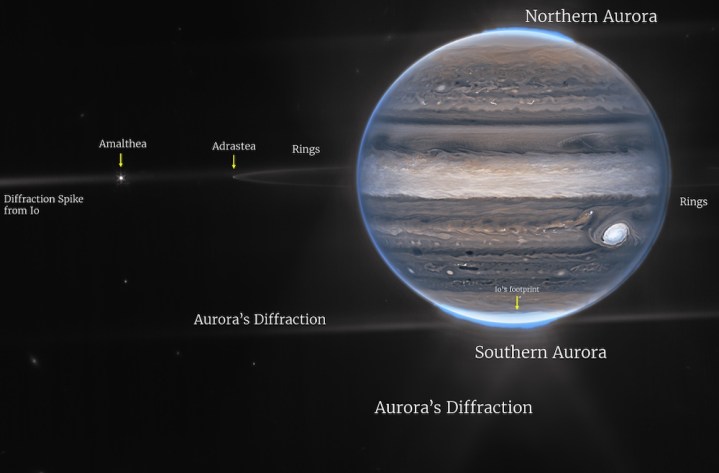
Captured by the Webb telescope’s Near-Infrared Camera (NIRCam), the image highlights gorgeous auroras extending to high altitudes above both the northern and southern poles of the planet.
The infrared light captured by the camera is invisible to the human eye, so the Webb team — working with citizen scientist Judy Schmidt — mapped the data in a way to make the details stand out. This explains why Jupiter’s distinctive Great Red Spot — a storm system described as “so big it could swallow Earth” — appears as white in the image.
The captured images are clearly way beyond what the Webb team had been hoping for.
“We hadn’t really expected it to be this good, to be honest … it’s really remarkable,” planetary astronomer Imke de Pater, who helped lead the observation, said in a post on NASA’s website.
After further analysis of the extraordinary image, Heidi Hammel, Webb interdisciplinary scientist for solar system observations, noted: “The brightness here indicates high altitude — so the Great Red Spot has high-altitude hazes, as does the equatorial region. The numerous bright white ‘spots’ and ‘streaks’ are likely very high-altitude cloud tops of condensed convective storms.”
In a wider image (below) captured by the Webb telescope, two tiny moons called Amalthea and Adrastea are visible.
After launching from Earth in December 2021, the Webb telescope — the most powerful ever built — is now in an orbit around a million miles away. NASA and its partners in Europe and Canada recently shared the first set of high-resolution color images from a mission that scientists believe could tell us more about the origins of the universe. It’s also searching for distant planets that could support life.
Other dazzling images captured by Webb include this this stunner showing the Cartwheel Galaxy located around 500 million light-years away in the Sculptor constellation.


