The planets in our solar system experience seasons because of the way that they are tilted in their orbits, so one hemisphere is facing the sun more often at some times of year than others. However, there’s another factor which also affects weather and conditions on some planets, which is their position in their orbit around the sun. Earth has a relatively circular orbit, so the differences caused by it being slightly closer or further from the sun at different points are minimal. But Mars’s orbit is much more eccentric or oval-shaped than Earth’s, meaning conditions differ based on when the planet is closer to the sun.
That effect is illustrated in two images of Mars recently released by NASA, which show the planet at its closest and furthest point from the sun. Taken by a Mars orbiter called MAVEN, or Mars Atmosphere and Volatile EvolutioN, the images were taken six months apart in July 2022 and January 2023 respectively, showing how the environment of the planet changes with both season and the planet’s orbit.
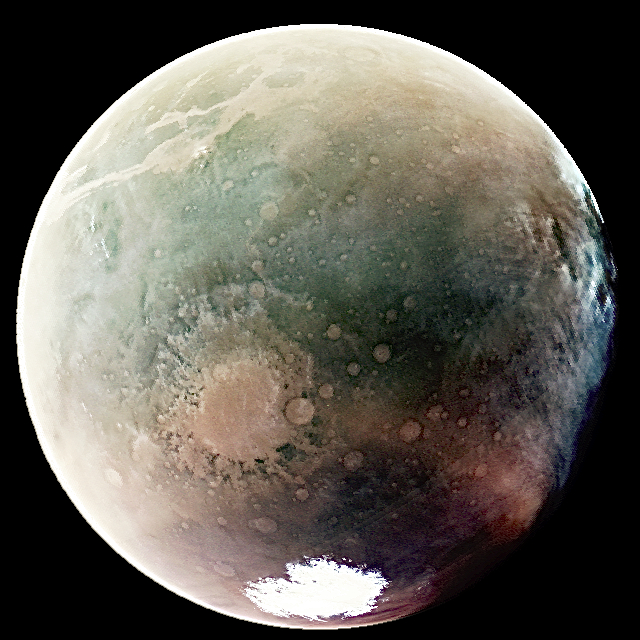

This first image was taken during the summer season on the planet’s southern hemisphere when Mars was at its closest point to the sun. The image was taken by MAVEN’s Imaging Ultraviolet Spectrograph (IUVS) instrument, which operates in the ultraviolet wavelength. So to create an image, the values from the instrument have to be shifted into the visible light range.
This helps to pick out key features of the image like atmospheric ozone which appears in purple. It’s also why the surface of the planet appears green in places, even though the actual planet appears red or orange when photographed in the visible light wavelength. At the bottom of the planet, you can see the southern polar ice cap, which has shrunk in the relatively warm summer weather.
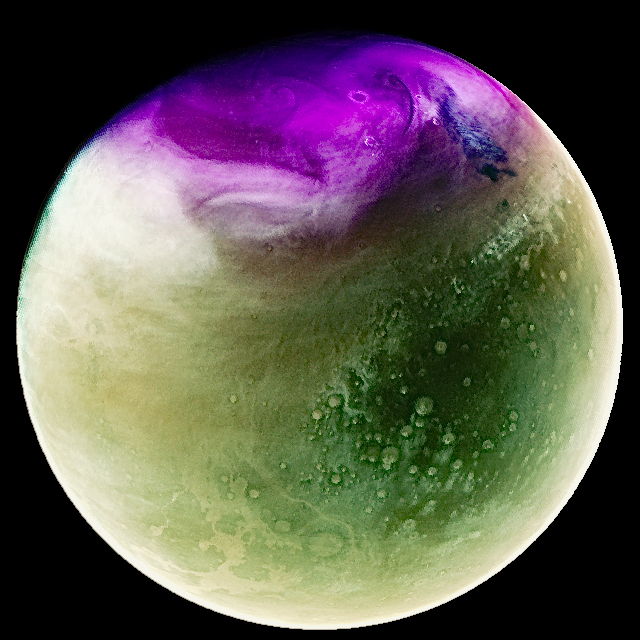
This second image, showing Mars’s northern hemisphere, was taken when the planet had passed its furthest point from the sun. Here you can see the bright purple cap of ozone across the entire north pole. This ozone is formed over the winter months when carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is broken up by sunlight. When spring arrives, the ozone reacts with water vapor and is destroyed.
MAVEN is used to study Mars’s atmosphere and weather and has previously researched how water vapor is sucked up from polar ice caps during the summer and how this is affected by the large dust storms which periodically roll across the planet.



