NASA’s first-ever spacecraft mission took place 64 years ago this week, though it didn’t quite work out as planned.
Pioneer 1 launched from Cape Canaveral on October 11, 1958, and was intended to orbit the moon in a mission that came three months after NASA was founded.
The aim was to study the ionizing radiation, cosmic rays, magnetic fields, and micrometeorites close to Earth and also in lunar orbit.
However, following the spacecraft’s launch on a Thor-Able rocket, the velocity of its push toward the moon wasn’t strong enough, preventing it from reaching our nearest neighbor. Two days later, Pioneer 1 came to a fiery end as it burned up in Earth’s atmosphere.
It wasn’t all bad news, though, as, during its brief outing, the spacecraft managed to beam back to scientists around 43 hours’ worth of data on near-Earth’s atmosphere.
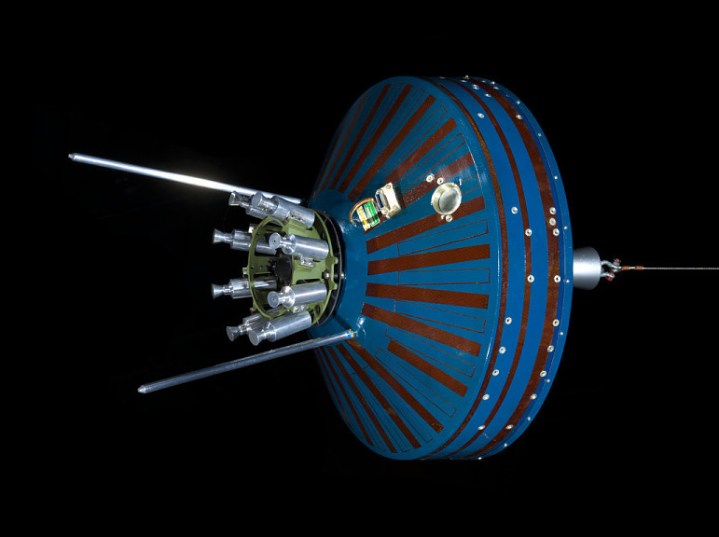
Pioneer 1 was a relatively small space vehicle featuring a cylindrical midsection 29.1 inches (74 centimeters) in diameter and a height of 30 inches (76 centimeters). At one end protruded an 11 kg solid propellant injection rocket and rocket case, while eight smaller low-thrust solid propellant velocity adjustment rockets were also attached in a ring formation.
The spacecraft carried with it a scanning infrared television system intended for studying the moon’s surface, a diaphragm/microphone assembly to detect micrometeorites, a spin-coil magnetometer to measure magnetic fields, and temperature-variable resistors to record spacecraft internal conditions.
A newspaper report filed shortly after the spacecraft’s launch captured some of the buzz surrounding the mission, opening with: “America’s moon rocket stirred vast excitement around the earth Saturday.” The report went on to say that many people were surprised by the mission because “few thought American scientists would get so near [to] success on their second try,” referencing the non-NASA Pioneer 0 mission that crashed and burned shortly after launch a few months earlier.
Highlighting the Cold War between East and West at the time, the report described the mission as a “spectacular Western achievement to weigh against the loudly trumpeted Sputnik successes of the Soviet Union.”
NASA learned a great deal from its early Pioneer missions, paving the way for gradually more ambitious voyages to deep space. The final one in the program, Pioneer 11, left Earth in 1973 and made the first direct observations of Saturn six years later. While communications with Pioneer 11 have long been lost, NASA says it’s heading toward the constellation of Aquila (The Eagle) and is on course to pass near one of the stars in the constellation in about 4 million years’ time.


